kottke.org posts about art

The International Exhibition of Modern Art held at the The 69th Regiment Armory in NYC in 1913 was the first large public exhibition of modern art in the US. It has become known simply as The Armory Show. Among the artists represented at the show were Paul Cézanne, Georges Braque, Georges Seurat, Vincent van Gogh, Auguste Rodin, Pablo Picasso, Wassily Kandinsky, Claude Monet, Marcel Duchamp, Henri Matisse, and Fernand Léger. So yeah, important show.
John Ptak noticed in a book he was reading that the sales total for the show was $44,148, which is something like $1,000,000 in today’s dollars. Of that total, two artists were responsible for almost a third of the total: Odilon Redon made $7000 and Cézanne made $6700. Duchamp sold four pieces for $972. It goes without saying that the ~1600 pieces exhibited at The Armory Show would fetch billions of dollars at auction now.
On the walk back from soccer practice the other day, my sharp-eyed seven-year-old son spotted something through the partially papered-up window of a Chelsea gallery. “Hey, Kara Walker!” he says.1 And sure enough:
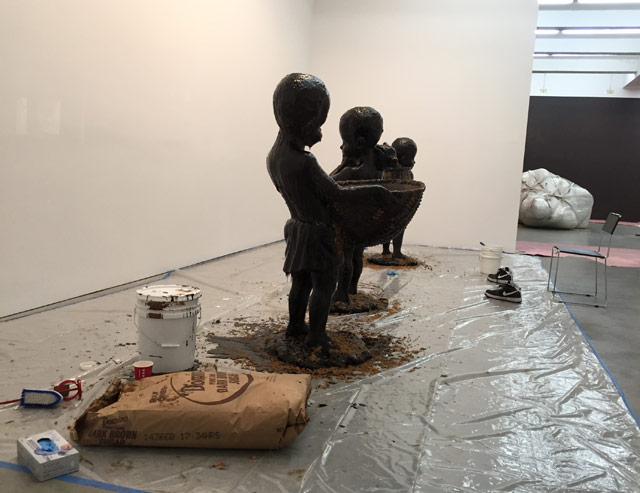

The gallery is Sikkema Jenkins on 22nd St and Walker’s show, Afterword, starts there tomorrow and runs through mid-January. The show is an extension of A Subtlety, Walker’s installation at the Domino Sugar Factory in Williamsburg over the summer. Several of the sugar statues and the left fist of the sugar sphinx from the Domino installation will be shown along with new video works and notes & sketches from the planning of A Subtlety. You can see some of the figures in the photo above (fashioned out of Domino Sugar, naturally) and I think that’s probably the fist in the background on the right, wrapped in plastic.
Klaus Kemp is one of the last great practitioners of arranging diatoms, tiny single celled algae. The art is only visible under microscopic magnification.
More information about Kemp and his images is available on his web site. (via waxy)
Everyone knows graffiti artist extraordinaire Banksy is a man. What this post presupposes is, maybe she’s a woman?
But what Banksy Does New York makes plain is that the artist known as Banksy is someone with a background in the art world. That someone is working with a committee of people to execute works that range in scale from simple stencil graffiti to elaborate theatrical conceits. The documentary shows that Banksy has a different understanding of the street than the artists, street-writers, and art dealers who steal Banksy’s shine by “spot-jocking” or straight-up pilfering her work-swagger-jackers who are invariably men in Banksy Does New York.
All of which serves as evidence against the flimsy theory that Banksy is a man.
Or maybe Banksy’s like the Dread Pirate Roberts?
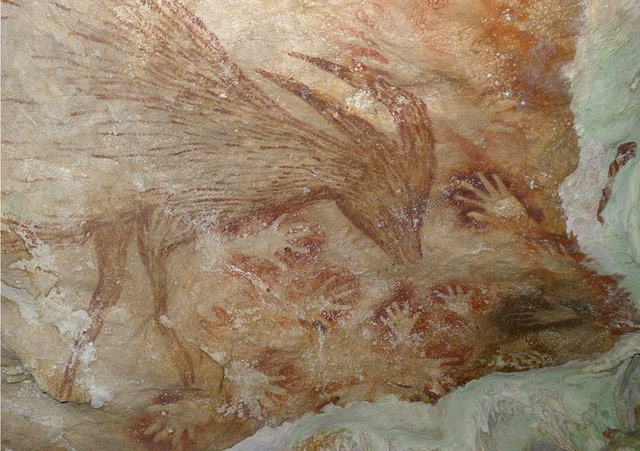

Paintings in a cave in Indonesia have been dated to 40,000 years ago, as old or older than any paintings found in Europe.
For decades, the only evidence of ancient cave art was in Spain and southern France. It led some to believe that the creative explosion that led to the art and science we know today began in Europe.
But the discovery of paintings of a similar age in Indonesia shatters this view, according to Prof Chris Stringer of the Natural History Museum in London.
“It is a really important find; it enables us to get away from this Euro-centric view of a creative explosion that was special to Europe and did not develop in other parts of the world until much later,” he said.
The discovery of 40,000-year-old cave paintings at opposite ends of the globe suggests that the ability to create representational art had its origins further back in time in Africa, before modern humans spread across the rest of the world.
“That’s kind of my gut feeling,” says Prof Stringer. “The basis for this art was there 60,000 years ago; it may even have been there in Africa before 60,000 years ago and it spread with modern humans”.
New work from Olafur Eliasson: he installed a riverbed in the Louisiana Museum of Modern Art in Denmark.

Take a closer look at how half-a-dozen ceramics masters practice their craft.
People are taking photos of statues that cleverly make it look as though the statues are taking selfies.
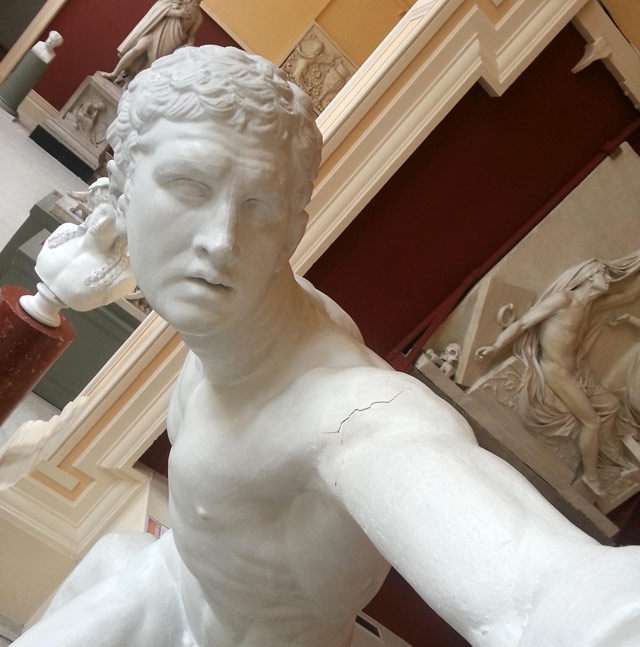

There’s a group on Reddit but most of the photos really aren’t that good. There are more examples on Instagram, including this one and this one from June that predate the activity on Reddit. But the earliest instances I found of statue selfies were this Instagram photo from The Art Institute of Chicago and this tweet featuring the Statue of Liberty, both from December 2013.
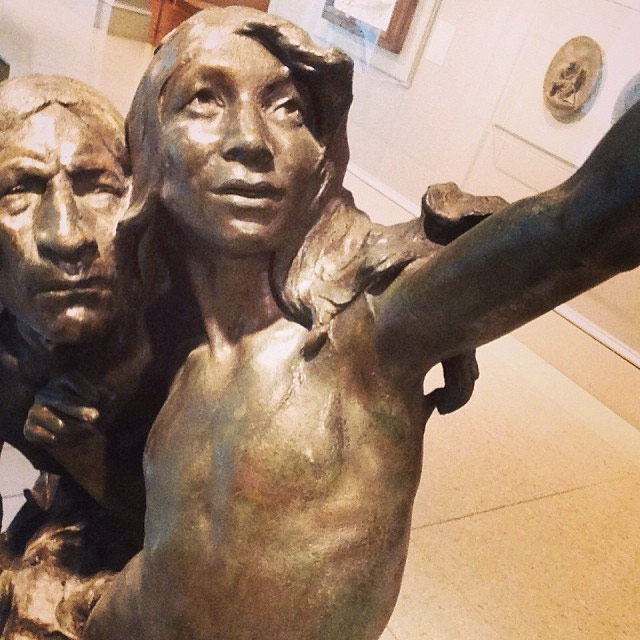

(via @ThatAmelia)
Update: See also Museum of Selfies.

Watch Peanuts creator Charles Schulz draw Charlie Brown. It only takes him around 35 seconds.
(via @fchimero)
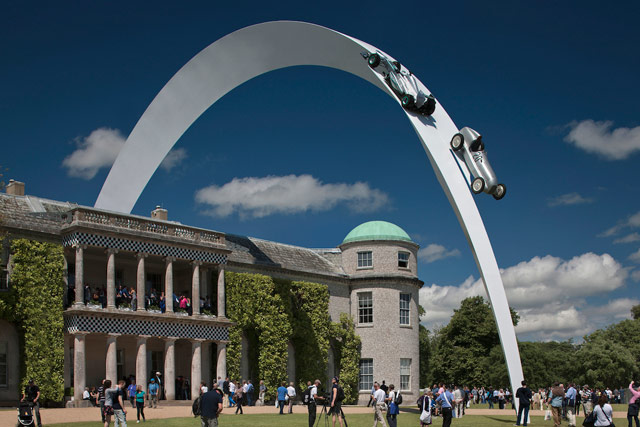
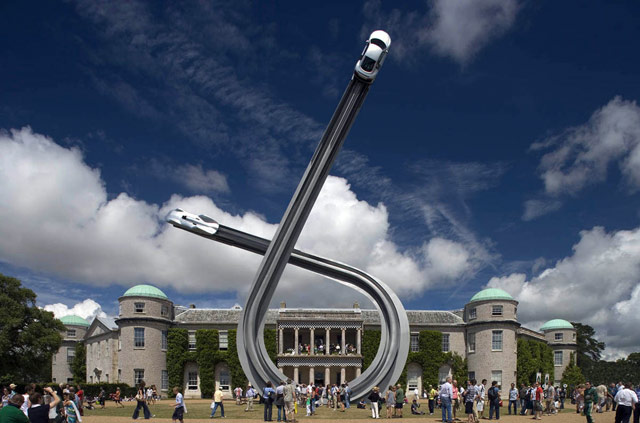
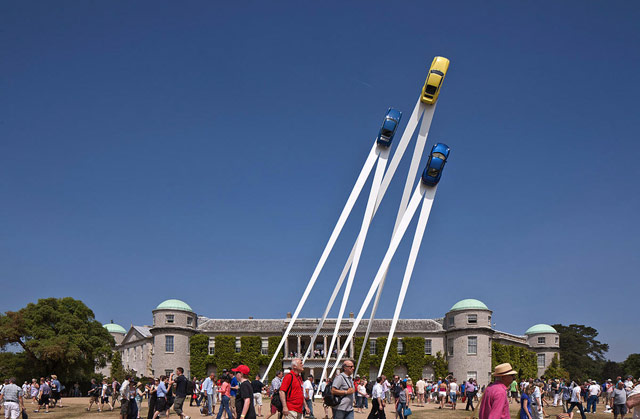



These sculptures by Gerry Judah for the Goodwood Festival of Speed are amazing. Here’s how they made the Mercedes arch for this year’s festival. (via ministry of type)
A seller on Chinese b2b site Alibaba is offering stainless steel sculptures of balloon animal dogs in the style of Jeff Koons. For as little as $500, you can get your own knock-off copy of Balloon Dog, which sold for $58 million last year.
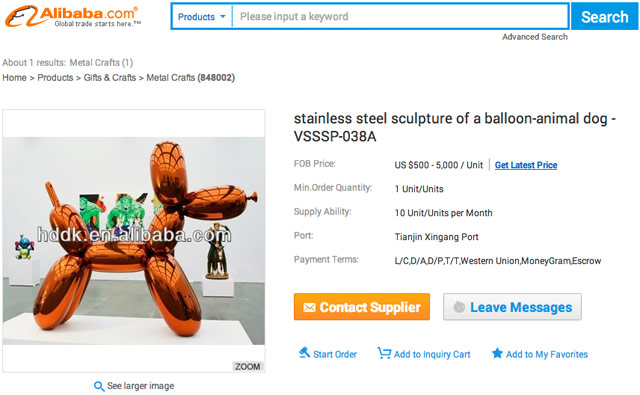
Koons’ dog was about 10 feet tall but the seller notes they can make them anywhere from 3 feet tall to almost 100 feet tall. Jiminy. I wonder what these things look like? I bet they aren’t nearly as precise as the originals, but you never know. See also: Rex Sorgatz’s Uber for Art Forgeries. (via prosthetic knowledge)
Walking City is a slowly evolving walking video sculpture by Universal Everything. A walking tour of modern architecture, if you will.
File this one under mesmerizing. A deserving winner of the Golden Nica award at Ars Electronica. (via subtraction)
In the first two installments of a series about artistic authenticity, Rex Sorgatz writes about five different people’s efforts to own a Vermeer and how you can get your very own masterpiece.
It’s possible that Vermeer — an artist who many consider the greatest painter of all time — could paint with no more acuity than you or me. Vermeer may have been a simple technologist — but a technologist who could recreate the world with scintillating photographic intensity, centuries before photography was invented, which might actually be a bigger deal than being a good painter.
I loved these articles. I wish I would have written them…I am fascinated with both Vermeer and art forgeries. Good stuff.
Sometime around 1918 in Buenos Aires, Marcel Duchamp designed a chess set:
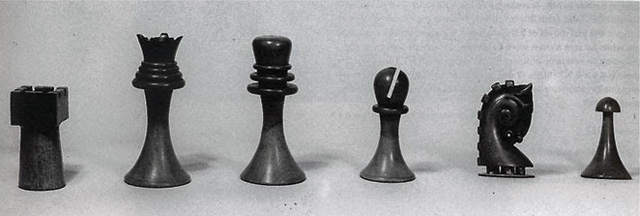
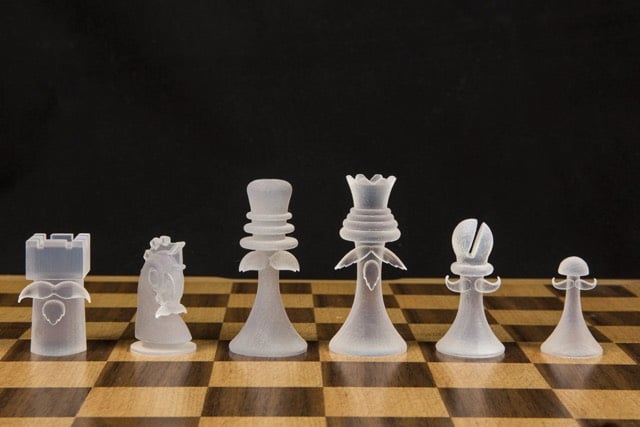
Sometime earlier this year, Scott Kildall and Brian Sera used archival photos of the hard-to-find set, turned them into 3D models of the chess pieces, and made a pattern for 3D printing your own set:

The community at Thingaverse is already busy making interesting variations of Duchamp’s set…look at this one:

Something tells me Duchamp would have loved this whole thing.
Update: Welllllll, Duchamp may have loved this, but his estate definitely did not. Duchamp’s estate sent Kildall and Sera a cease and desist letter, forcing them to remove the 3D models from Thingiverse. Which, the irony! So, Kildall and Sera, riffing on Duchamp’s mustachioed Mona Lisa, have created a set of six 3D-printed chess pieces with mustaches modeled on the Duchamp set. Fantastic.

From the official Chuck Jones Tumblr, an early sketch of the Road Runner and Coyote by Jones.
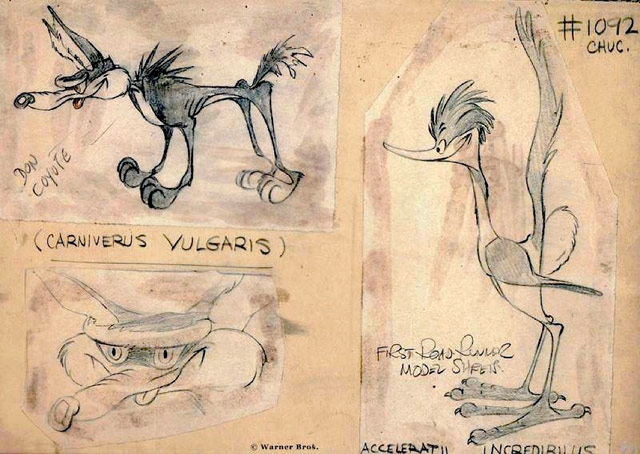
Also by Jones, how to draw Bugs Bunny:
(via @peeweeherman)
When he was around 32 years old, Leonardo da Vinci applied to the Duke of Milan, Ludovico Sforza, for a job. The duke was in need of military expertise and Leonardo’s 10-point CV emphasized his military engineering skills:
3. Also, if one cannot, when besieging a terrain, proceed by bombardment either because of the height of the glacis or the strength of its situation and location, I have methods for destroying every fortress or other stranglehold unless it has been founded upon a rock or so forth.
4. I have also types of cannon, most convenient and easily portable, with which to hurl small stones almost like a hail-storm; and the smoke from the cannon will instil a great fear in the enemy on account of the grave damage and confusion.
And I love what is almost an aside at the end of the list:
Also I can execute sculpture in marble, bronze and clay. Likewise in painting, I can do everything possible as well as any other, whosoever he may be.
Oh yeah, P.S., by the way, not that it matters, I am also the greatest living artist in the world, no big deal. Yr pal, Leo. (via farnam street and the letters of note book)
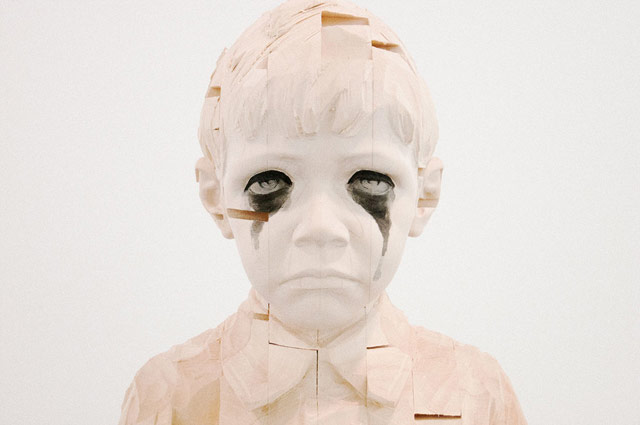

Clayton Cubitt took photographs of The Beautifully Frightful Wooden Children of Gehard Demetz, now on display at Jack Shainman Gallery in Chelsea. From the gallery’s description of the project:
With impeccable craftsmanship, Demetz builds figures and reliefs of children and rural, often religious, architectural forms. While his subjects often take the forms of adolescent or very young children who are at the precipice of self-realization, their grave expressions and powerful stances suggest something much less innocent than their ages might suggest. Situated on plinths, these life-size works are elevated above their natural stature, allowing them to confront adults at eye level with a fierce or introspective gaze far beyond their years. Rather than being carved from a single large block of wood, these sculptures are built up from smaller rectangular units-mimicking classic building blocks-with gaps in their structures like pieces missing from their bodies or lost fragments of their being.

NYC’s Metropolitan Museum of Art has made a whopping 400,000 high-resolution digital images of its collection available for free download. You can browse the collection here.
In making the announcement, Mr. Campbell said: “Through this new, open-access policy, we join a growing number of museums that provide free access to images of art in the public domain. I am delighted that digital technology can open the doors to this trove of images from our encyclopedic collection.”
The Metropolitan Museum’s initiative-called Open Access for Scholarly Content (OASC)-provides access to images of art in its collection that the Museum believes to be in the public domain and free of other known restrictions; these images are now available for scholarly use in any media.
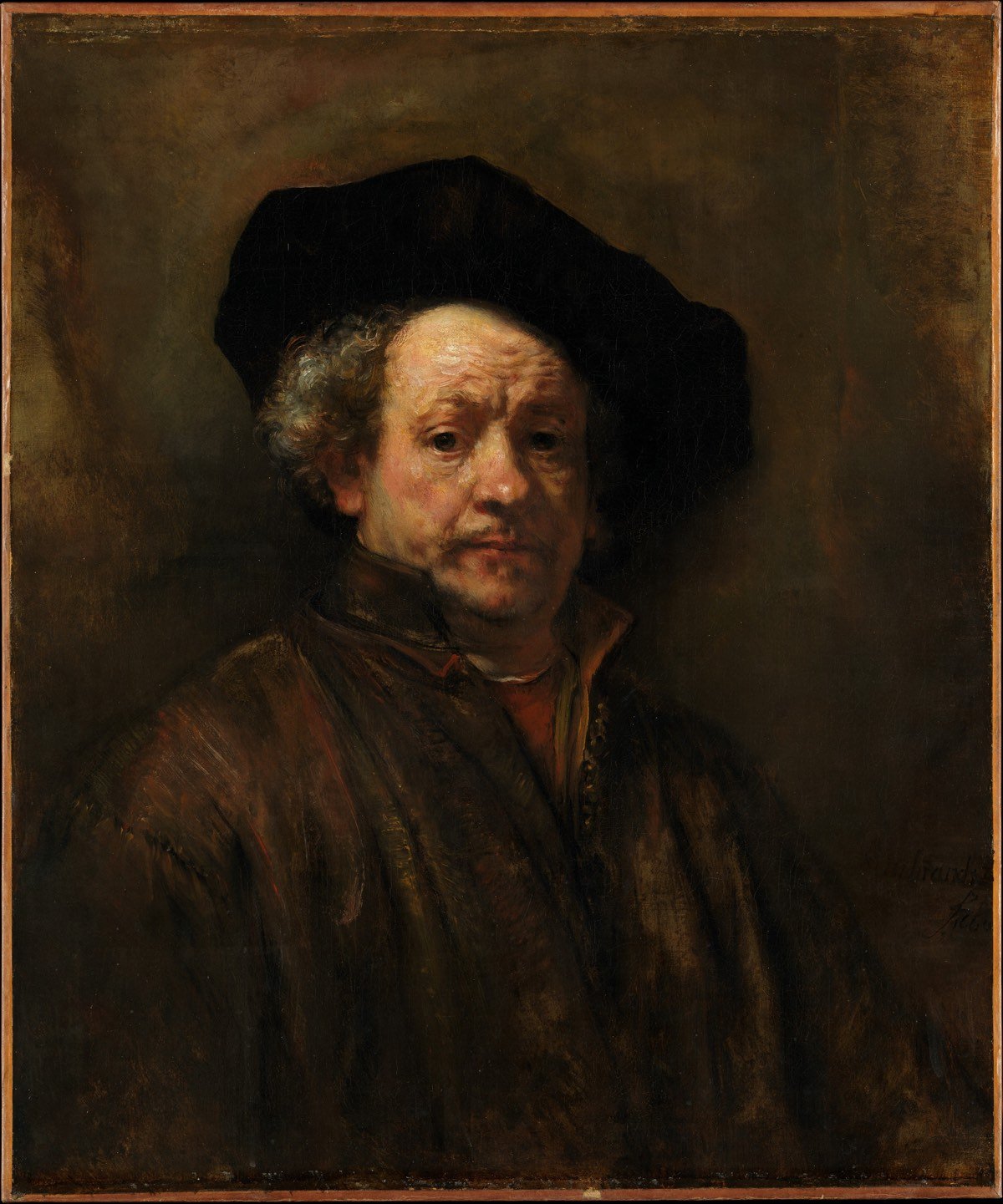
For instance, here’s a 12-megapixel image of Rembrandt’s 1660 self-portrait…you can see quite a bit of detail:
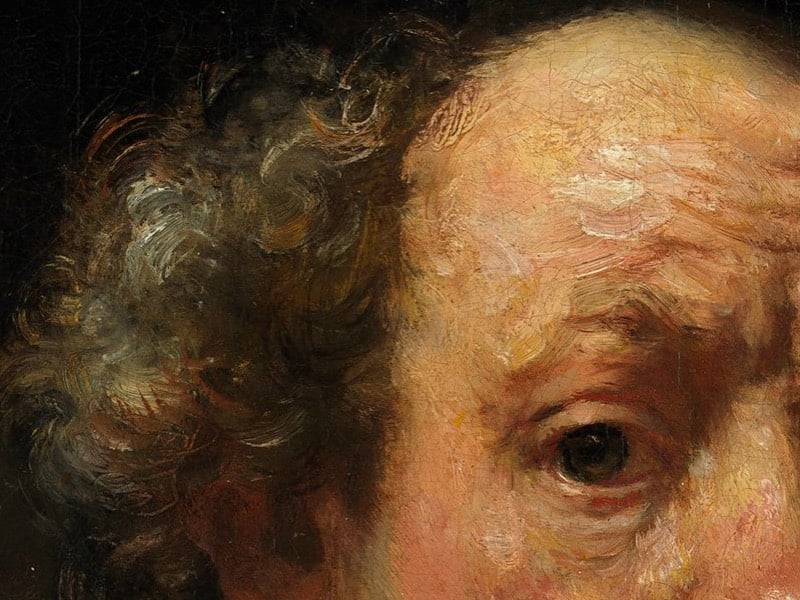

(thx, fiona)
Update: Wendy Macnaughton on why the high-resolution images released by the Met are such a big deal for art students and art history fans.
For someone who went to art school being able to do this is a revelation. I used to go to the museum with my sketchpad and copy the old masters. I’d get as close as I could to understand the brush strokes, colors, lines. The guards knew who to watch out for and would bark suddenly when we stuck our faces over the imaginary line.
As class assignments we were required to copy hundreds — literally hundreds — of the masters drawings and paintings. for those we mostly worked from images in books — a picture the size of a wallet photo.
Which is one of the many reasons this new met resource is fucking phenomenal.
You can get so, so close — far closer than one could in real life.
Update: Today (Feb 7, 2017) the Met announced that they’re releasing 375,000 images under Creative Commons’ CC0 license, which “allows anyone to use, re-use, and remix a work without restriction”. Previously, those works were restricted to non-commercial use only.
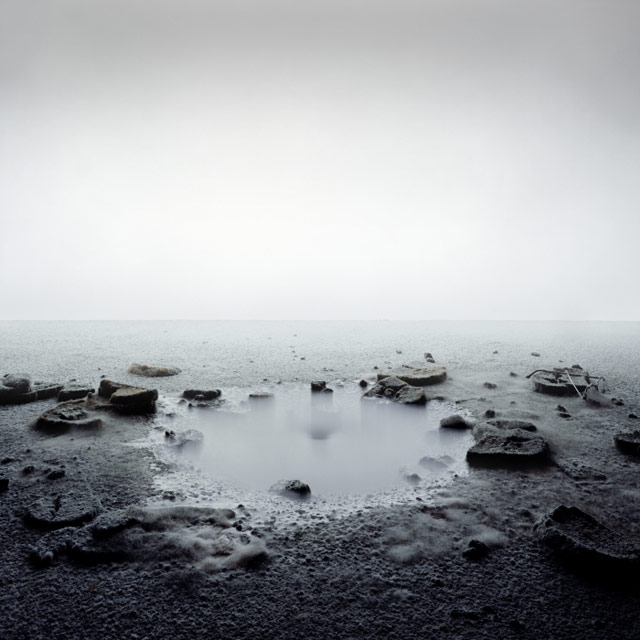
Swedish artist Hans Jörgen Johansen makes photographs of mold landscapes, grown in his studio from flour and bread.
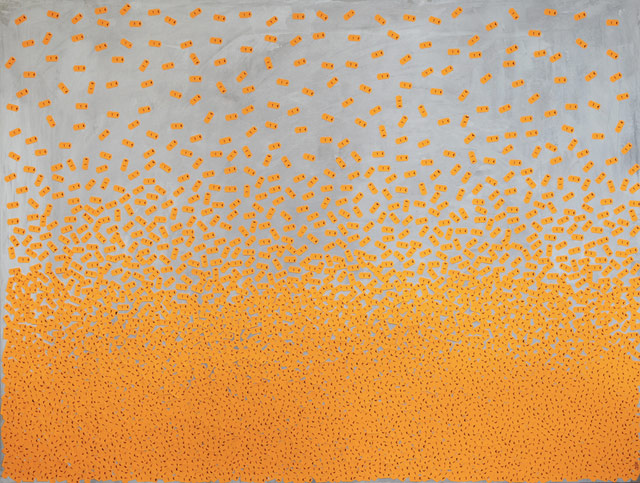


French artist BL67 makes his works by sticking price tags directly to the canvas. Each piece is priced according to the total of the price stickers stuck to it. Here’s a close-up showing some detail:

(via adam)
Man, I really like these paintings from Jeremy Mann’s Cityscape series. Particularly the NYC street scenes, like this one in Hell’s Kitchen:

Mann’s paintings seem to hold a lot of detail, even up close, but there are also broader strokes visible only from afar. Not sure if that’s novel (unlikely) but I haven’t seen it elsewhere. (via colossal)
Swiss artist Zimoun used a bunch of fans and packing peanuts to make it look like an angry foaming ocean inside this building:
Zimoun’s piece is on display through July 11 at la Limonaia di Villa Saroli in Lugano, Switzerland. (via coudal)

In the 1980s, when personal computers with graphics capabilities were first introduced, Andy Warhol was an enthusiastic early adopter. In 1985, Commodore commissioned the artist to produce some art on their Amiga computer, but the work was never widely shown and was assumed lost. Then artist and retro computer nerd Cory Arcangel learned of Warhol’s Amiga experiments from this video (and perhaps this article from a 1986 issue of Amigaworld) and set in motion the process of finding out if any of the computers or storage devices in The Andy Warhol Museum contained his Amiga art.
CMU Computer Club members determined that even reading the data from the diskettes entailed significant risk to the contents, and would require unusual tools and methodologies. By February 2013, in collaboration with collections manager Amber Morgan and other AWM personnel, the Club had completed a plan for handling the delicate disk media, and gathered at The Andy Warhol Museum to see if any data could be extracted. The Computer Club set up a cart of exotic gear, while a video crew from the Hillman Photography Initiative, under the direction of Kukielski, followed their progress.
It was not known in advance whether any of Warhol’s imagery existed on the floppy disks-nearly all of which were system and application diskettes onto which, the team later discovered, Warhol had saved his own data. Reviewing the disks’ directory listings, the team’s initial excitement on seeing promising filenames like “campbells.pic” and “marilyn1.pic” quickly turned to dismay, when it emerged that the files were stored in a completely unknown file format, unrecognized by any utility. Soon afterwards, however, the Club’s forensics experts had reverse-engineered the unfamiliar format, unveiling 28 never-before-seen digital images that were judged to be in Warhol’s style by the AWM’s experts. At least eleven of these images featured Warhol’s signature.
Incredible.
It’s been suggested that perhaps Johannes Vermeer painted his exacting masterpieces with the help of mirrors and lenses. Tim Jenison learned of these suggestions and started to study the problem.
He was in no rush. His R&D period lasted five years. He went to the Rijksmuseum in Amsterdam. “Looking at their Vermeers,” he says, “I had an epiphany” — the first of several. “The photographic tone is what jumped out at me. Why was Vermeer so realistic? Because he got the values right,” meaning the color values. “Vermeer got it right in ways that the eye couldn’t see. It looked to me like Vermeer was painting in a way that was impossible. I jumped into studying art.”
A recent documentary called Tim’s Vermeer (directed by Penn & Teller’s Teller) follows Jenison’s quest to construct a contraption that allows someone to paint as Vermeer did. Here’s a trailer:
Not sure you can find the movie in theaters anymore, but it should be out on DVD/download soon.
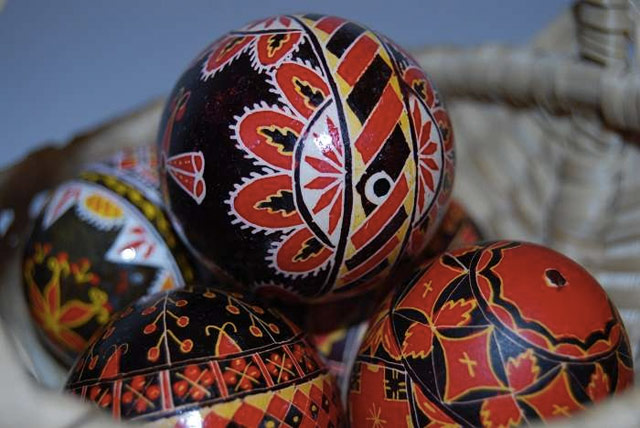

The small village of Ciocanesti in Romania produces the most beautiful hand-painted Easter eggs I’ve ever seen. This video is a wonderful look at the process and tradition.
Here’s how it works:
First, the (duck, goose, chicken, or even ostrich) egg is drained, through a tiny hole. Then, using a method akin to batik, it is dipped in dye and painted one color at a time, with the painter applying beeswax to those areas she wants to protect from the next round of dying. The painting implement, called a kishitze, is a stick with an iron tip. (Previously, egg-painters would have used thorns or pig bristles.)
And then the wax is melted and wiped off the egg, revealing the colors underneath. So cool. (via @colossal)
In a five part series called “emoji-nation”, Ukrainian Nastya Ptichek mixes the work of well-known painters with graphical elements of new media. In the second part of the series, the works of Edward Hopper are augmented with social media interface icons:

The first part finds emoji doppelgangers for works of fine art while the third part uses paintings as movie poster imagery for the likes of Kill Bill and Home Alone (paired with Munch’s The Scream). For part four, Ptichek places modal dialogs over art works:
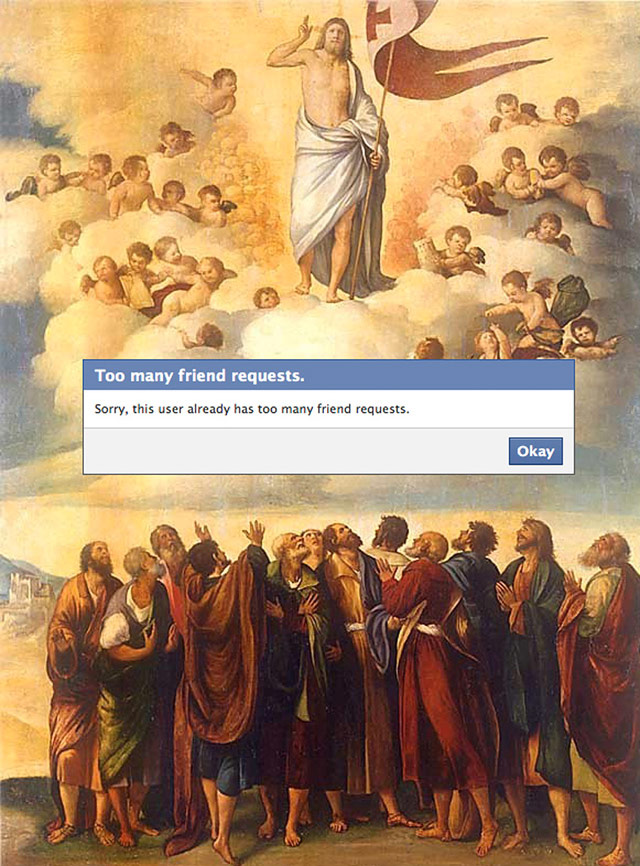
And part five plays around with several Google interface elements:

Love this kind of thing. Feels like I’ve seen something like it before though. Anyone recall?
Ben Sack makes these amazingly detailed maps of cities, all drawn by hand.
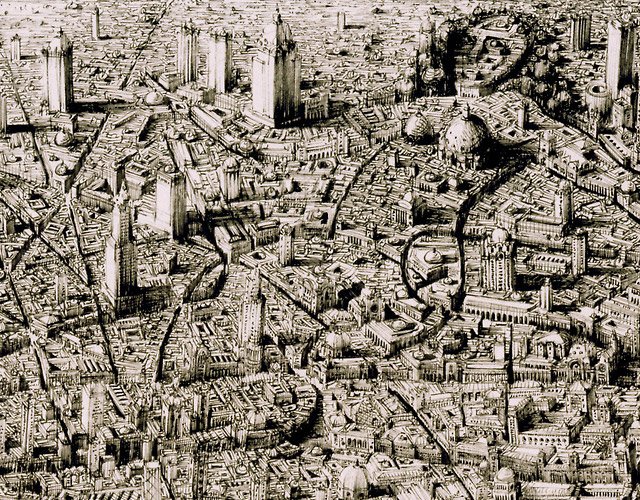
And just so you can get a sense of how large these drawings are:
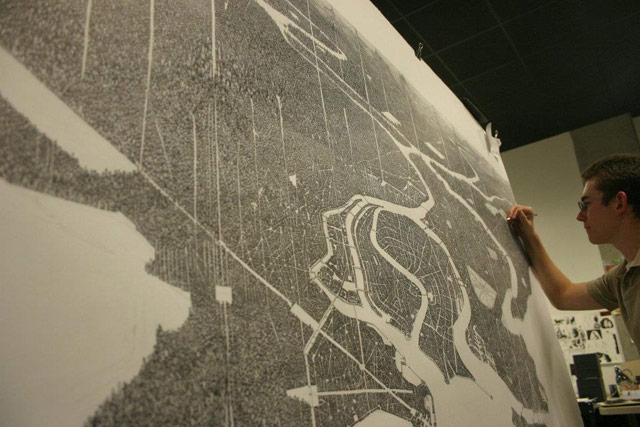

Here’s a peek at his process:
Reminiscent of Stephen Wiltshire’s work. And every time I see something like this, I think about when I went to the Met a few years ago and noticed the sketchbook of this guy working the membership desk. It was filled with beautifully intricate drawings of NYC-style city streets. I chatted with him about them briefly, but I wish I’d asked if he had put any of it online. Would have been neat to share his drawings with you. (via waxy)
Newer posts
Older posts






































Socials & More