kottke.org posts about CIA
For Wired’s series Technique Critique, former CIA Chief of Disguise Jonna Mendez looks at several TV shows and movies to rate how good their spy scenes are.
Mendez gives high marks to characters from Alias and The Americans for effective use of disguises and low marks to The Bourne Identity and Homeland. In relation to Philip’s disguises on The Americans, she discusses the concept of the little gray man, the CIA’s goal for its agents to look like harmless middle-aged men, something she also mentioned in this Washington Post piece:
Rhys makes the case, however, for disappearing under nothing more than a knit cap and a pair of glasses, a scruffy mustache and a messy wig. He becomes the consummate little gray man, invisible, the one nobody can remember was even on the elevator.
Mendez also talks about the three cover identities that CIA agents were not allowed to use: clergy, media figures, and Peace Corps volunteer. She previously did this video with Wired about how the CIA used disguises.
In this video, Jonna Mendez, the former Chief of Disguise of the CIA, explains how disgu — Wait, wait, wait…Chief of Disguise!! That is an actual job title!?! WHAT! Ok, back to the post… — explains how disguises are used in the CIA.
With women, you have a broader range of what you can do. You also have one extra step: you can turn a woman into a man. I would mention that it’s almost impossible to turn a man into a woman. What we do is always additive — we can make you taller, we can make you heavier, we can make you older — we can’t go the other direction. You want to be the person that gets on the elevator and then gets off and nobody even remembers that you were really there. That is a design goal at the disguise labs at CIA.
Interesting throughout. As a fan of the disguises on The Americans and as someone who got to wear some bitchin’ makeup for a short extra appearance on Halt and Catch Fire, I really enjoyed this video, but now I’m wondering what my “dead giveaway” mannerisms are. Friends, any thoughts?

In 1944, the OSS (the precursor to the CIA) produced a document called the Simple Sabotage Field Manual (PDF). It was designed to be used by agents in the field to hinder our WWII adversaries. The CIA recently highlighted five tips from the manual as timelessly relevant:
1. Managers and Supervisors: To lower morale and production, be pleasant to inefficient workers; give them undeserved promotions. Discriminate against efficient workers; complain unjustly about their work.
2. Employees: Work slowly. Think of ways to increase the number of movements needed to do your job: use a light hammer instead of a heavy one; try to make a small wrench do instead of a big one.
3. Organizations and Conferences: When possible, refer all matters to committees, for “further study and consideration.” Attempt to make the committees as large and bureaucratic as possible. Hold conferences when there is more critical work to be done.
4. Telephone: At office, hotel and local telephone switchboards, delay putting calls through, give out wrong numbers, cut people off “accidentally,” or forget to disconnect them so that the line cannot be used again.
5. Transportation: Make train travel as inconvenient as possible for enemy personnel. Issue two tickets for the same seat on a train in order to set up an “interesting” argument.
Ha, some of these things are practically best practices in American business, not against enemies but against their employees, customers, and themselves. You can also find the manual in book or ebook format. (via @craigmod)
In a series of tweets this morning, surgeon and author Atul Gawande called out the doctors who helped the CIA torture people.
First do no harm.
This is disgusting and awful and monstrous and I don’t even know what to say about it. The NY Times lists seven key points (full article) from a report released by the Senate Select Committee on Intelligence about the CIA’s torture practices. We knew it was bad, suspected it was worse, but this is just beyond.
The report describes extensive waterboarding as a “series of near drownings” and suggests that more prisoners were subjected to waterboarding than the three prisoners the C.I.A. has acknowledged in the past. The report also describes detainees being subjected to sleep deprivation for up to a week, medically unnecessary “rectal feeding” and death threats. Conditions at one prison, described by a clandestine officer as a “dungeon,” were blamed for the death of a detainee, and the harsh techniques were described as leading to “psychological and behavioral issues, including hallucinations, paranoia, insomnia, and attempts at self-harm and self-mutilation.”
This is surely the shit sandwich on top of an already unbearable year. I agree wholeheartedly with Vermont Senator Bernie Sanders, who issued this statement about the report:
A great nation must be prepared to acknowledge its errors. This report details an ugly chapter in American history during which our leaders and the intelligence community dishonored our nation’s proud traditions. Of course we must aggressively pursue international terrorists who would do us harm, but we must do so in a way that is consistent with the basic respect for human rights which makes us proud to be Americans.
“The United States must not engage in torture. If we do, in an increasingly brutal world we lose our moral standing to condemn other nations or groups that engage in uncivilized behavior.
From a 1995 article in The Independent, an account of how the CIA promoted and funded US and other Western artists during the Cold War, including abstract expressionists like Rothko and Pollock.
The decision to include culture and art in the US Cold War arsenal was taken as soon as the CIA was founded in 1947. Dismayed at the appeal communism still had for many intellectuals and artists in the West, the new agency set up a division, the Propaganda Assets Inventory, which at its peak could influence more than 800 newspapers, magazines and public information organisations. They joked that it was like a Wurlitzer jukebox: when the CIA pushed a button it could hear whatever tune it wanted playing across the world.
The next key step came in 1950, when the International Organisations Division (IOD) was set up under Tom Braden. It was this office which subsidised the animated version of George Orwell’s Animal Farm, which sponsored American jazz artists, opera recitals, the Boston Symphony Orchestra’s international touring programme. Its agents were placed in the film industry, in publishing houses, even as travel writers for the celebrated Fodor guides. And, we now know, it promoted America’s anarchic avant-garde movement, Abstract Expressionism.
(via @sippey)
The Boston Globe has a slideshow with a few examples from the now-declassified Official CIA Manual of Trickery and Deception.
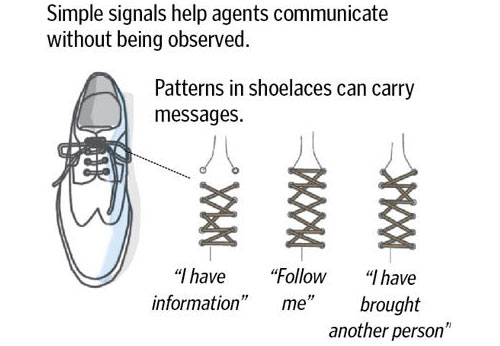
Here’s the associated article. One could imagine a Mad Men/Bond-style spy show set in the 1960s that would utilize these techniques.






Socials & More