
This Aeon essay by Giorgio van Straten, “Lost in Migration,” is excerpted from a book titled In Search of Lost Books, which explains its fascination with a book that’s fascinated many people, a manuscript carried in a briefcase by Walter Benjamin at the end of his life which has never been identified or located and probably did not survive him.
I’ve always been a little turned off by the obsession with this manuscript among Benjamin fans and readers. There’s something so shattering to me about the end of Benjamin’s life, and how he died, that it feels not just trivial, but almost profane to geek out over the imaginary contents of a book he might have left behind. I feel the same way about dead musicians. It’s all just bad news.
Luckily, though, this essay does contain a compelling and concise account of the end of Benjamin’s life.
First Benjamin fled Paris, which had been bombed and was nearly about to be invaded by the German army, for Marseilles:
Benjamin was not an old man - he was only 48 years old - even if the years weighed more heavily at the time than they do now. But he was tired and unwell (his friends called him ‘Old Benj’); he suffered from asthma, had already had one heart attack, and had always been unsuited to much physical activity, accustomed as he was to spending his time either with his books or in erudite conversation. For him, every move, every physical undertaking represented a kind of trauma, yet his vicissitudes had over the years necessitated some 28 changes of address. And in addition he was bad at coping with the mundane aspects of life, the prosaic necessities of everyday living.
Hannah Arendt repeated with reference to Benjamin remarks made by Jacques Rivière about Proust:
He died of the same inexperience that permitted him to write his works. He died of ignorance of the world, because he did not know how to make a fire or open a window.
before adding to them a remark of her own:
With a precision suggesting a sleepwalker his clumsiness invariably guided him to the very centre of a misfortune.
Now this man seemingly inept in the everyday business of living found himself having to move in the midst of war, in a country on the verge of collapse, in hopeless confusion.
From Marseilles he hoped to reach Spain, since, as a German refugee, he did not have the proper exit papers.
The next morning he was joined soon after daybreak by his travelling companions. The path they took climbed ever higher, and at times it was almost impossible to follow amid rocks and gorges. Benjamin began to feel increasingly fatigued, and he adopted a strategy to make the most of his energy: walking for 10 minutes and then resting for one, timing these intervals precisely with his pocket-watch. Ten minutes of walking and one of rest. As the path became progressively steeper, the two women and the boy were obliged to help him, since he could not manage by himself to carry the black suitcase he refused to abandon, insisting that it was more important that the manuscript inside it should reach America than that he should.
A tremendous physical effort was required, and though the group found themselves frequently on the point of giving up, they eventually reached a ridge from which vantage point the sea appeared, illuminated by the sun. Not much further off was the town of Portbou: against all odds they had made it.
Spain had changed its policy on refugees just the day before:
[A]nyone arriving ‘illegally’ would be sent back to France. For Benjamin this meant being handed over to the Germans. The only concession they obtained, on account of their exhaustion and the lateness of the hour, was to spend the night in Portbou: they would be allowed to stay in the Hotel Franca. Benjamin was given room number 3. They would be expelled the next day.
For Benjamin that day never came. He killed himself by swallowing the 15 morphine tablets he had carried with him in case his cardiac problems recurred.
This is how one of the greatest writers and thinkers of the twentieth century was lost to us, forever.
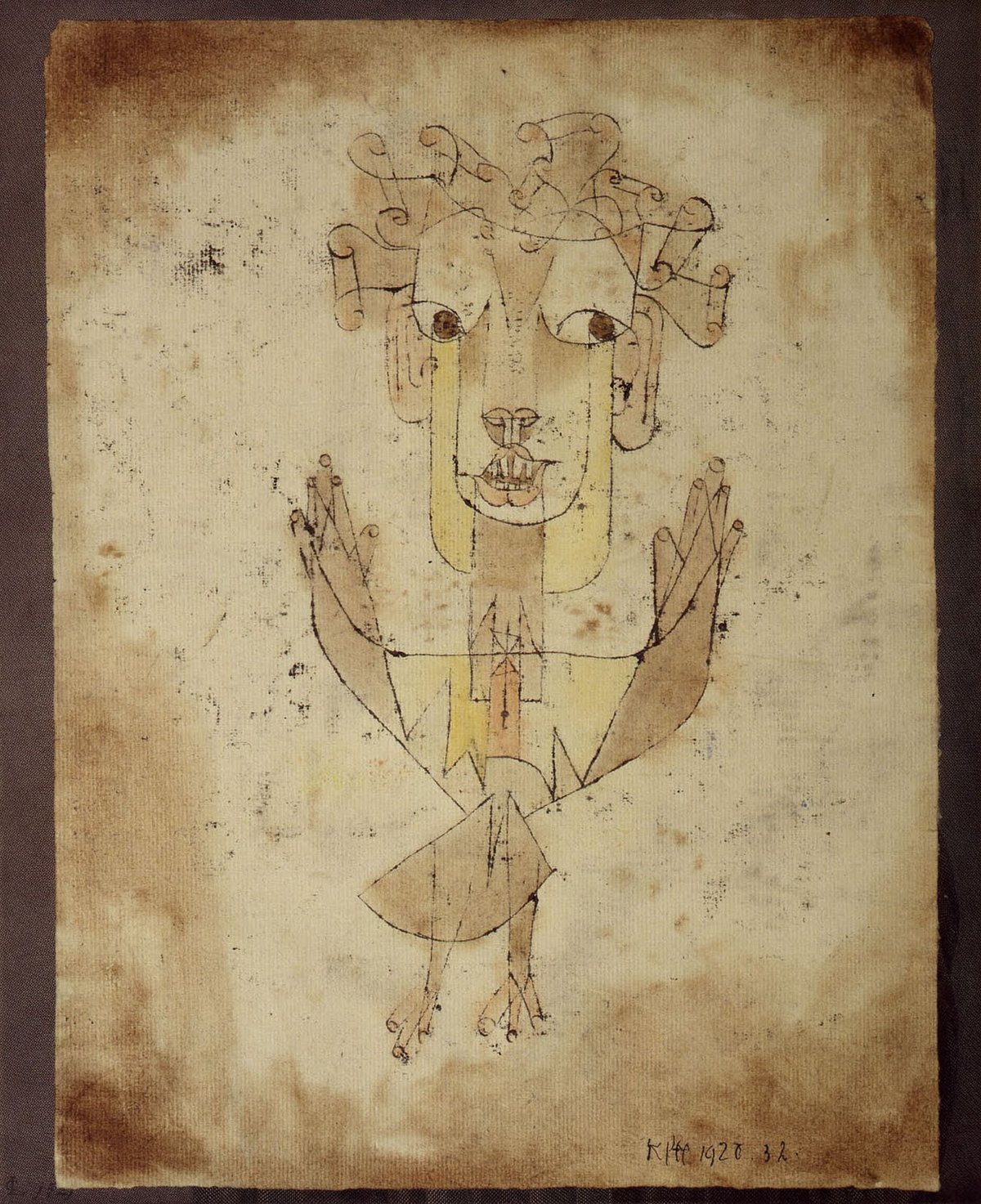

This is from Walter Benjamin’s essay “On the Concept of History,” but I’m going to use the old translation back when it was called “Theses on the Philosophy of History,” and mess with the line breaks a little. If you’ve read this a million times, forgive me; it’s always worth reading again.
A Klee painting named “Angelus Novus” shows an angel looking as though he is about to move away from something he is fixedly contemplating. His eyes are staring, his mouth is open, his wings are spread.
This is how one pictures the angel of history. His face is turned toward the past. Where we perceive a chain of events, he sees one single catastrophe which keeps piling wreckage and hurls it in front of his feet.
The angel would like to stay, awaken the dead, and make whole what has been smashed.
But a storm is blowing in from Paradise; it has got caught in his wings with such a violence that the angel can no longer close them. The storm irresistibly propels him into the future to which his back is turned, while the pile of debris before him grows skyward.
This storm is what we call progress.
Benjamin wrote this in 1940, in Paris; he’d left Germany shortly before the Nazis seized power. After the Nazis invaded France, he fled to Spain, with a precious travel visa to the United States. Spain’s government then cancelled all transit papers. The police told Benjamin and all the other Jewish refugees in his group would be returned to France. He killed himself.
His friend Hannah Arendt later made it across the border safely; she had the manuscript of this essay. Which is why it exists.
Why is this useful?
These are chaotic times. But to the angel of history, it’s not a sudden eruption of chaos, but a manifestation of an ongoing vortex of chaos that stretches back indefinitely, without any unique origin. When we’re thrust into danger, in a flash we get a more truthful glimpse of history than the simple narratives that suffice in moments of safety. As Benjamin puts it, “the tradition of the oppressed teaches us that the ‘state of emergency’ in which we live is not the exception but the rule.”
Global refugees, the stubborn pervasiveness of white supremacy, the arbitrary power of the state, the fragility of national and international institutions — we’ve been here for some time now, haven’t we? One day, you stir, and there you are — right where you’ve always been. With nothing under your feet, and ghosts pausing for breath next to your cheek.
This is not normal — and yet it’s the same as it’s always been. Because there is no normal. Not really. Just a series of accidents, a trick of the light, a collective hallucination we’ve all worked to diligently maintain.
Even now, most of us are working to impose an order on the world, to see a plan at work, to sort the chaos into “distractions” and “reality,” whether it’s “real news,” uncovering the secret aims of an unseen puppet master, or articulating the one true politics that can Fix Everything. We can’t help it; it’s what we do.
Remembering the angel helps ameliorate that impulse. Yes, there are opportunists everywhere, and real losses and victories, but the perfect theory that links events into beautiful chains of causality is elusive enough to be a dream for a fallen people. “Only a redeemed mankind receives the fullness of its past — which is to say, only for a redeemed mankind has its past become citable in all its moments.” For now, it’s all part of the storm; we’re all going to have to improvise.
For all his pessimism, rooted in a contempt and longing for a safety he couldn’t enjoy, Benjamin (I think) really did believe in the possibility of a Messiah, who would appear at a moment of great danger. It was a Jewish and a Marxist belief for someone who had great difficulty believing in either Judaism or Marxism in any of their existing forms.
There are a lot of people, on the left and the right, who share a version of this idea as a matter of dogma, without anything like the Kierkegaardian leap of faith Benjamin took in order to suspend his disbelief in it. Better to knock everything down, to build something new to replace it; heighten the stakes, so we have no choice but to take drastic steps to build paradise. I’m a lot less sure. I know what it took to build those things, and the emergencies that forced us to build them. It’s not an algebra problem to me, a clever lecture, a witty conjecture. I like those. Those are fun. This is not fun. This is blood and bones and broken things that do not come back. It would be nice to have a political or religious framework in which all those things can be mended or redeemed. It’s not available to me, except in its absence.
But for all that, I think I do believe in something smaller, more limited:
- I believe that moments of emergency are shot through with new possibilities;
- I believe there are more of us and there is more to us than we know;
- I think that we are always becoming something new;
- and this is because we don’t have a choice in the matter.
I think James Baldwin is right (Baldwin, like Benjamin, is somehow always right) when he writes in “Stranger in the Village” that while so many “American white men still nourish the illusion that there is some means of recovering the European innocence, of returning to a state in which black [and brown] men [and women] do not exist,” that
This is one of the greatest errors Americans can make. The identity they fought so hard to protect has, by virtue of that battle, undergone a change: Americans are as unlike any other white people in the world as it is possible to be. I do not think, for example, that it is too much to suggest that the American vision of the world — which allows so little reality, generally speaking, for any of the darker forces in human life, which tends until today to paint moral issues in glaring black and white — owes a great deal to the battle waged by Americans to maintain between themselves and black men a human separation which could not be bridged. It is only now beginning to be borne in on us — very faintly, it must be admitted, very slowly, and very much against our will— that this vision of the world is dangerously inaccurate, and perfectly useless. For it protects our moral high-mindedness at the terrible expense of weakening our grasp of reality. People who shut their eyes to reality simply invite their own destruction, and anyone who insists on remaining in a state of innocence long after that innocence is dead turns himself into a monster.
The time has come to realize that the interracial drama acted out on the American continent has not only created a new black man, it has created a new white man, too. No road whatever will lead Americans back to the simplicity of this European village where white men still have the luxury of looking on me as a stranger. I am not, really, a stranger any longer for any American alive. One of the things that distinguishes Americans from other people is that no other people has ever been so deeply involved in the lives of black men, and vice versa. This fact faced, with all its implications, it can be seen that the history of the American Negro problem is not merely shameful, it is also something of an achievement. For even when the worst has been said, it must also be added that the perpetual challenge posed by this problem was always, somehow, perpetually met. It is precisely this black-white experience which may prove of indispensable value to us in the world we face today. This world is white no longer, and it will never be white again.
In short, I believe in the future — not a paradise, not a tranquil place, not a reward, but in all its mundane possibility and broken uncertainty. I choose to believe in the future, simply because we have nowhere else to go.






Socials & More