The Sun, as Seen by the World’s Largest Solar Telescope
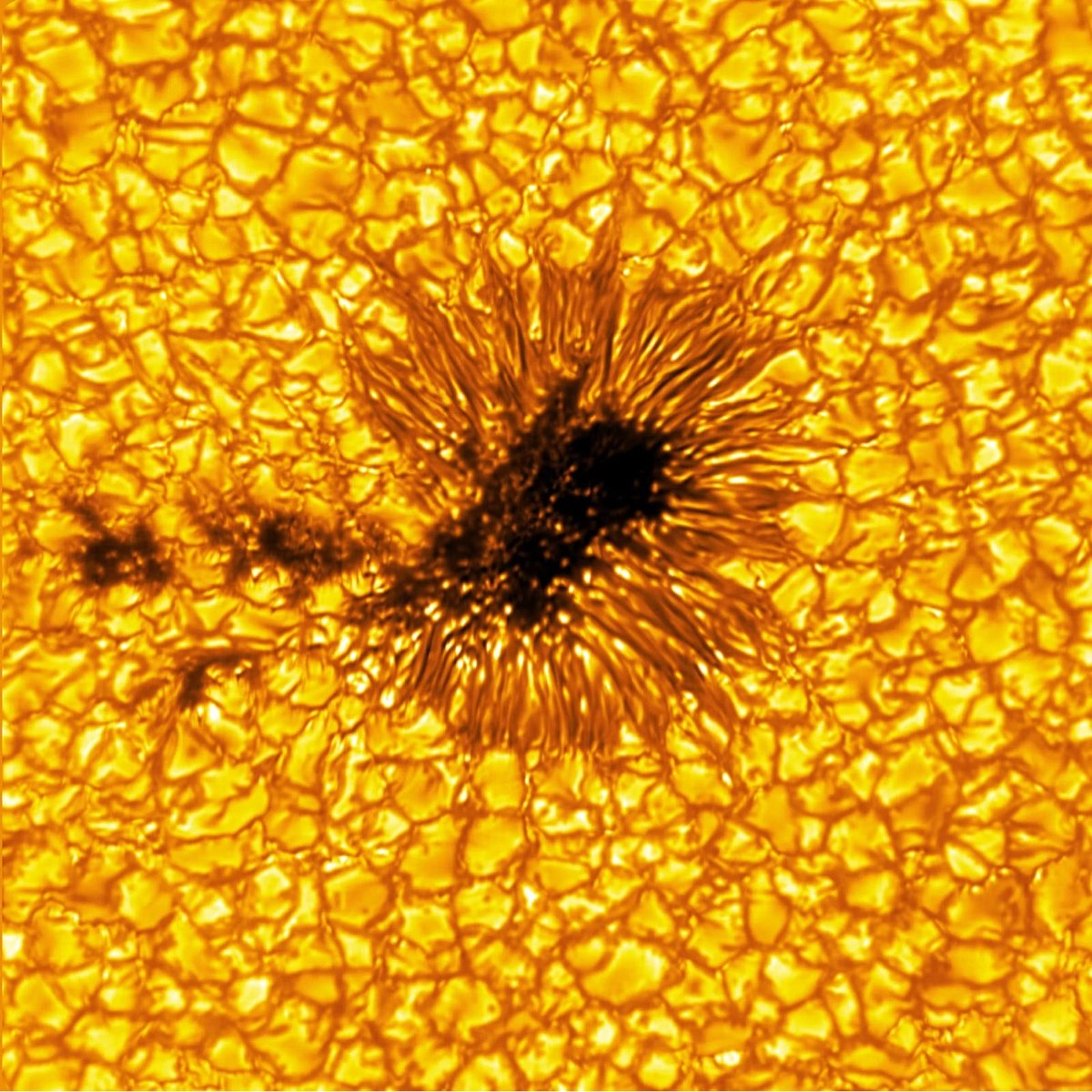
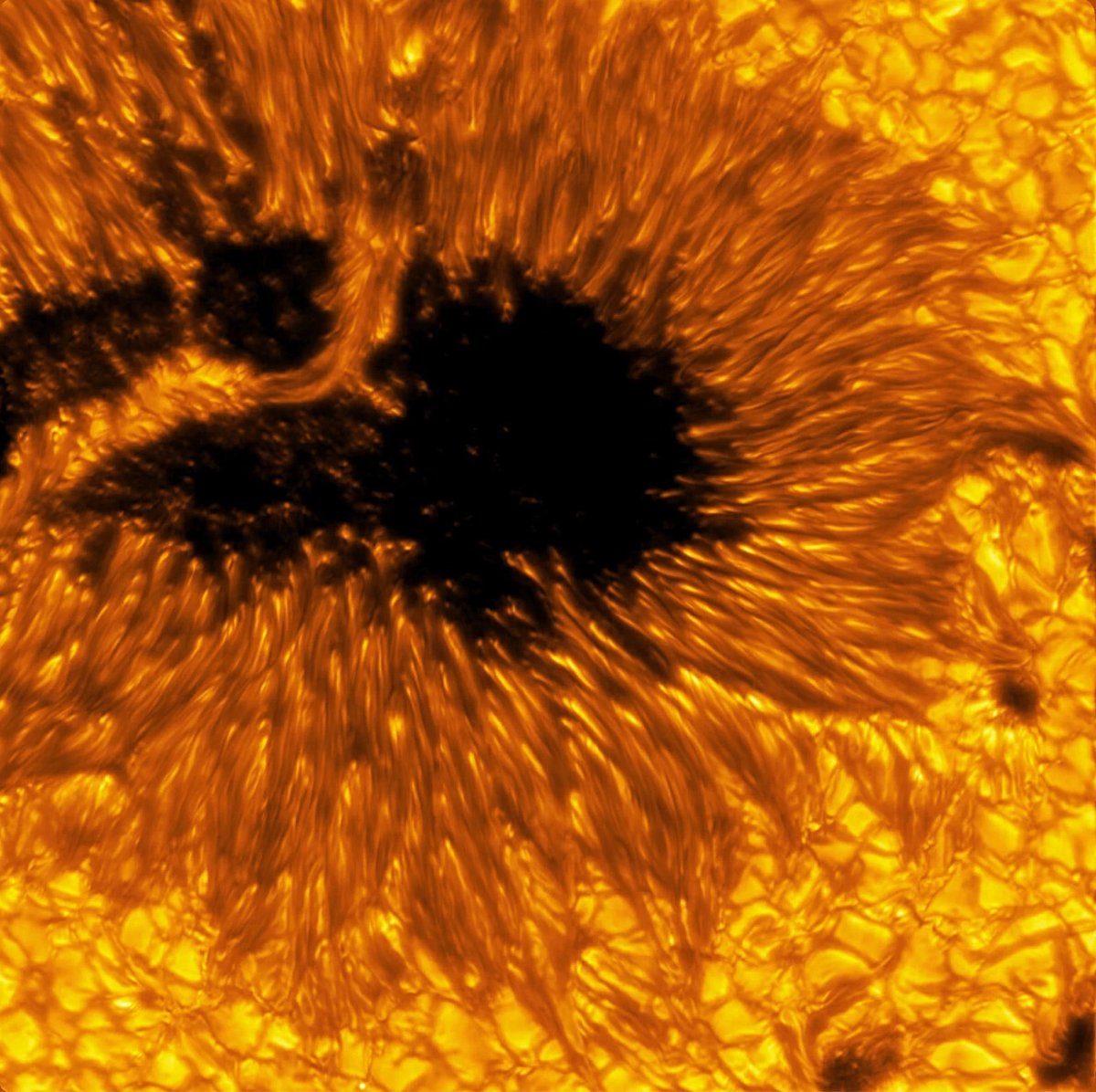
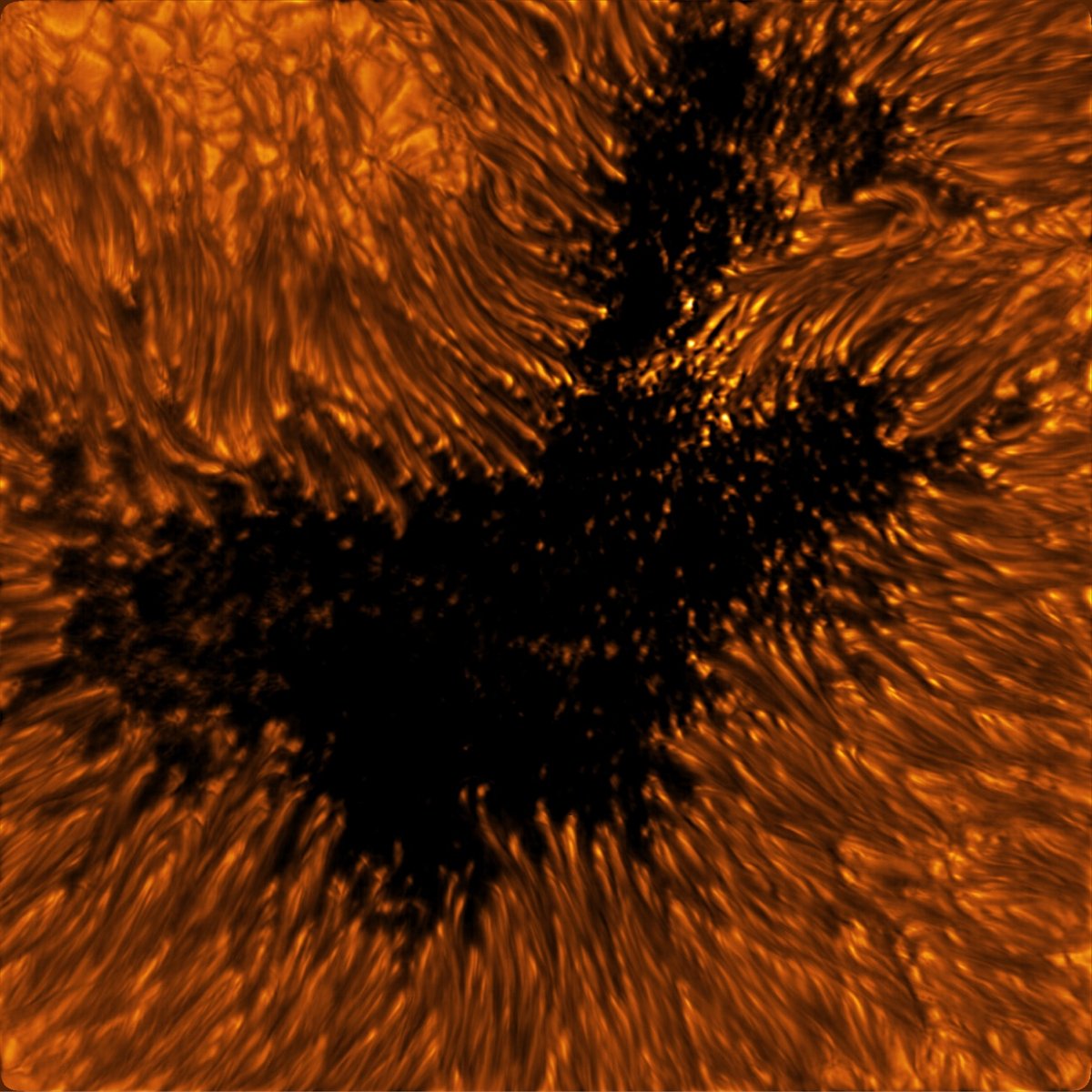
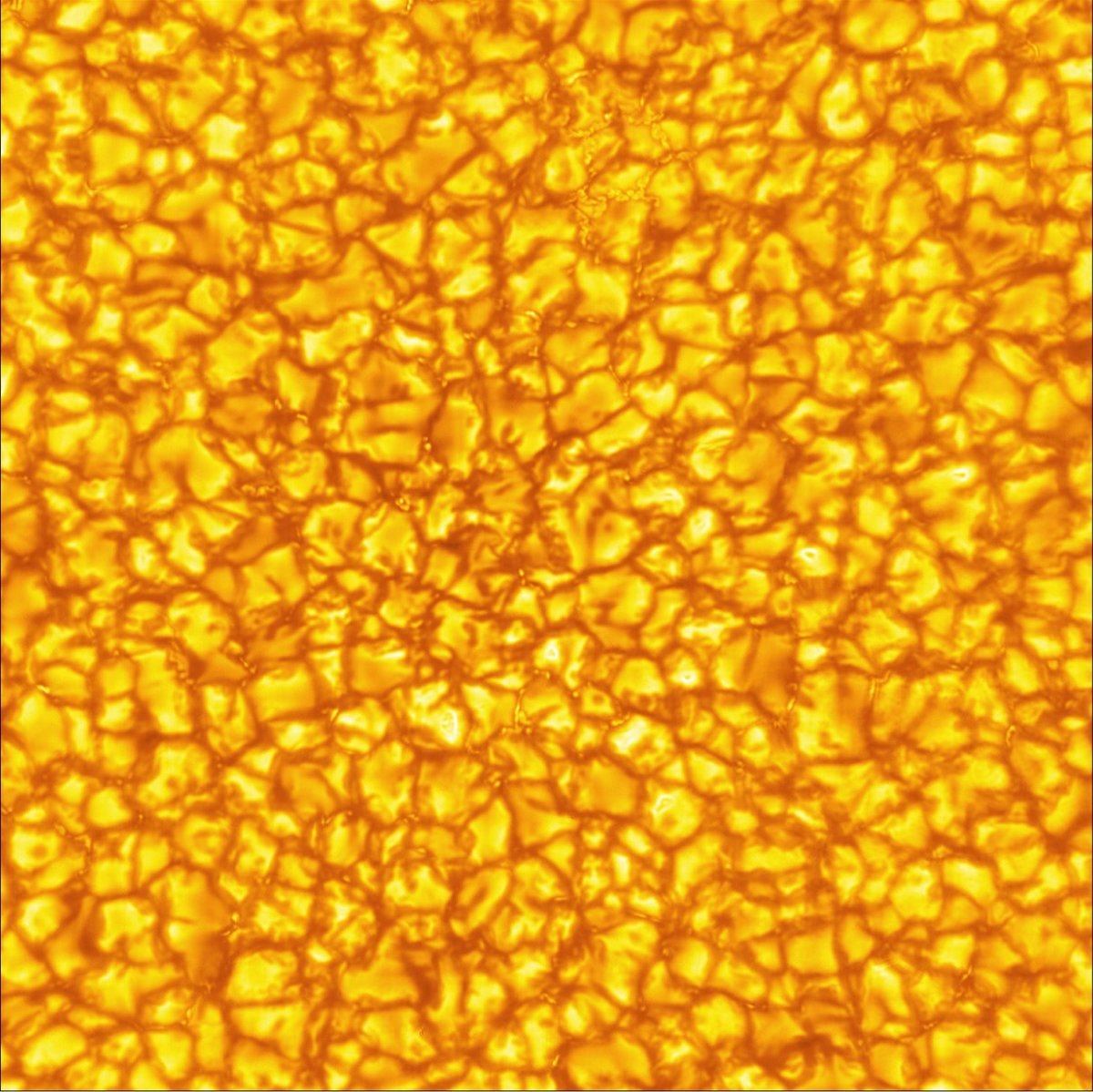
The Inouye Solar Telescope is the largest and most powerful solar telescope in the world. The telescope is still in a “learning and transitioning period” and not up to full operational speed, but scientists at the National Solar Observatory recently released a batch of images that hint at what it’s capable of. Several of the photos feature sunspots, cooler regions of the Sun with strong magnetic fields.
The sunspots pictured are dark and cool regions on the Sun’s “surface”, known as the photosphere, where strong magnetic fields persist. Sunspots vary in size, but many are often the size of Earth, if not larger. Complex sunspots or groups of sunspots can be the source of explosive events like flares and coronal mass ejections that generate solar storms. These energetic and eruptive phenomena influence the outermost atmospheric layer of the Sun, the heliosphere, with the potential to impact Earth and our critical infrastructure.
In the quiet regions of the Sun, the images show convection cells in the photosphere displaying a bright pattern of hot, upward-flowing plasma (granules) surrounded by darker lanes of cooler, down-flowing solar plasma. In the atmospheric layer above the photosphere, called the chromosphere, we see dark, elongated fibrils originating from locations of small-scale magnetic field accumulations.
(via petapixel)





Stay Connected