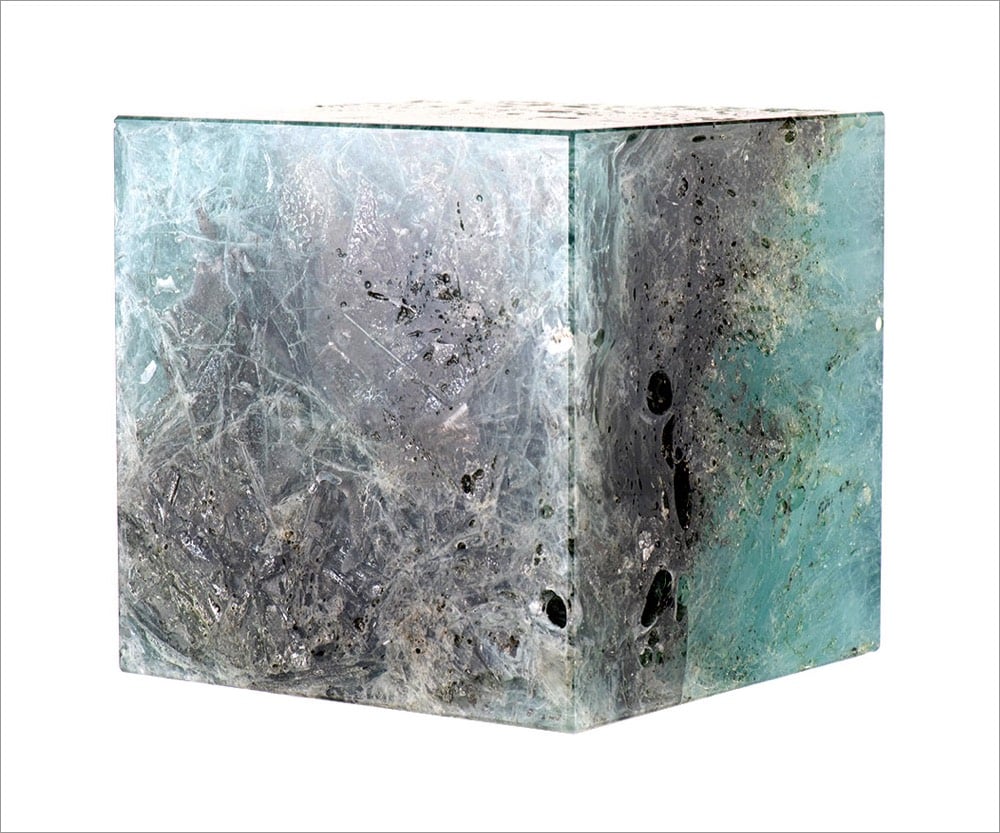
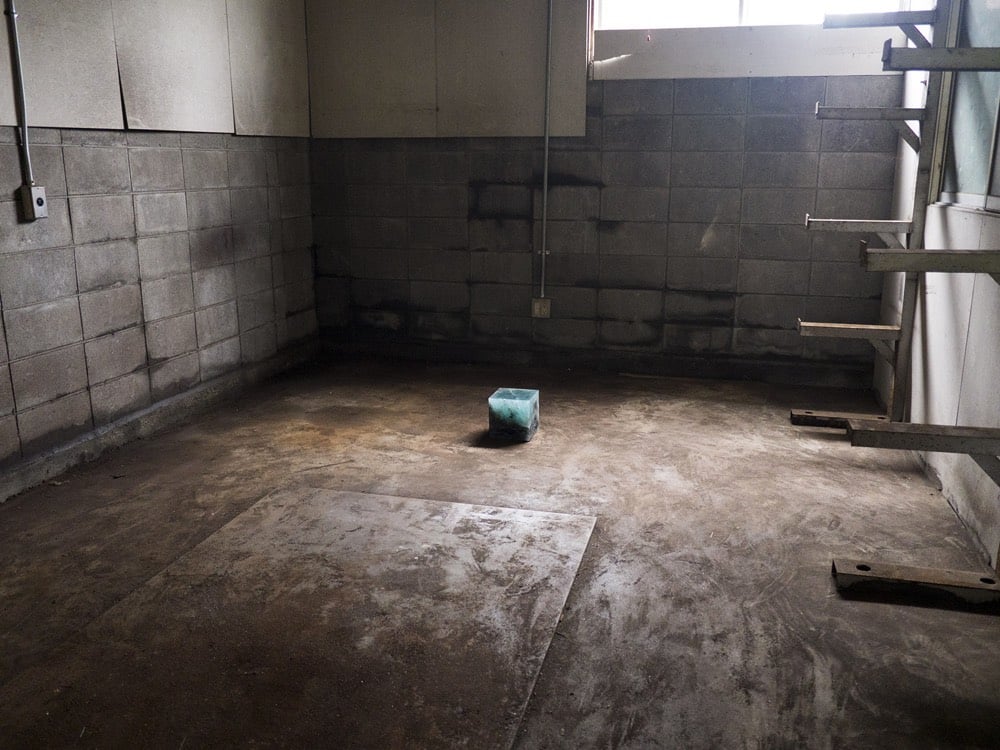


When the world’s first atomic weapon exploded in New Mexico in July 1945, the energy from the blast formed a new mineral called trinitite from the desert sand. For his 2015 Trinity Cube project, artist Trevor Paglen took irradiated glass gathered from the area around where the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster occurred in 2011 and combined it with trinitite to form a blue cube. He then installed the cube in the Fukushima Exclusion Zone to continue to be irradiated.
The artwork will be viewable by the public when the Exclusion Zone opens again, anytime between 3 and 30,000 years from the present.
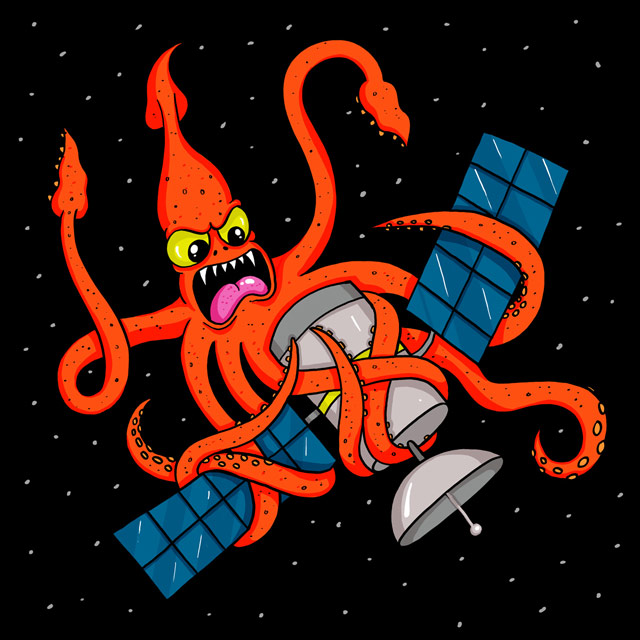

Trevor Paglen speculates that human civilization’s longest lasting monuments will be the satellites in geostationary orbits around the Earth.
Humanity’s longest lasting remnants are found among the stars. Over the last fifty years, hundreds of satellites have been launched into geosynchronous orbits, forming a ring of machines 36,000 kilometers from earth. Thousands of times further away than most other satellites, geostationary spacecraft remain locked as man-made moons in perpetual orbit long after their operational lifetimes. Geosynchronous spacecraft will be among civilization’s most enduring remnants, quietly circling earth until the earth is no more.
Geoff Manaugh attended a lecture of Paglen’s, where Paglen suggested a possible discoverer of these artifacts:
Billions of years from now, he began to narrate, long after city lights and the humans who made them have disappeared from the Earth, other intelligent species might eventually begin to see traces of humanity’s long-since erased presence on the planet.
Consider deep-sea squid, Paglen suggested, who would have billions of years to continue developing and perfecting their incredible eyesight, a sensory skill perfect for peering through the otherwise impenetrable darkness of the oceans — yet also an eyesight that could let them gaze out at the stars in deep space.
Perhaps, Paglen speculated, these future deep-sea squid with their extraordinary powers of sight honed precisely for focusing on tiny points of light in the darkness might drift up to the surface of the ocean on calm nights to look upward at the stars, viewing a scene that will have rearranged into whole new constellations since the last time humans walked the Earth.
And, there, the squid might notice something.
Note: Illustration by Chris Piascik…prints & more are available.







Socials & More