A Navajo Weaving of an Intel Pentium Processor
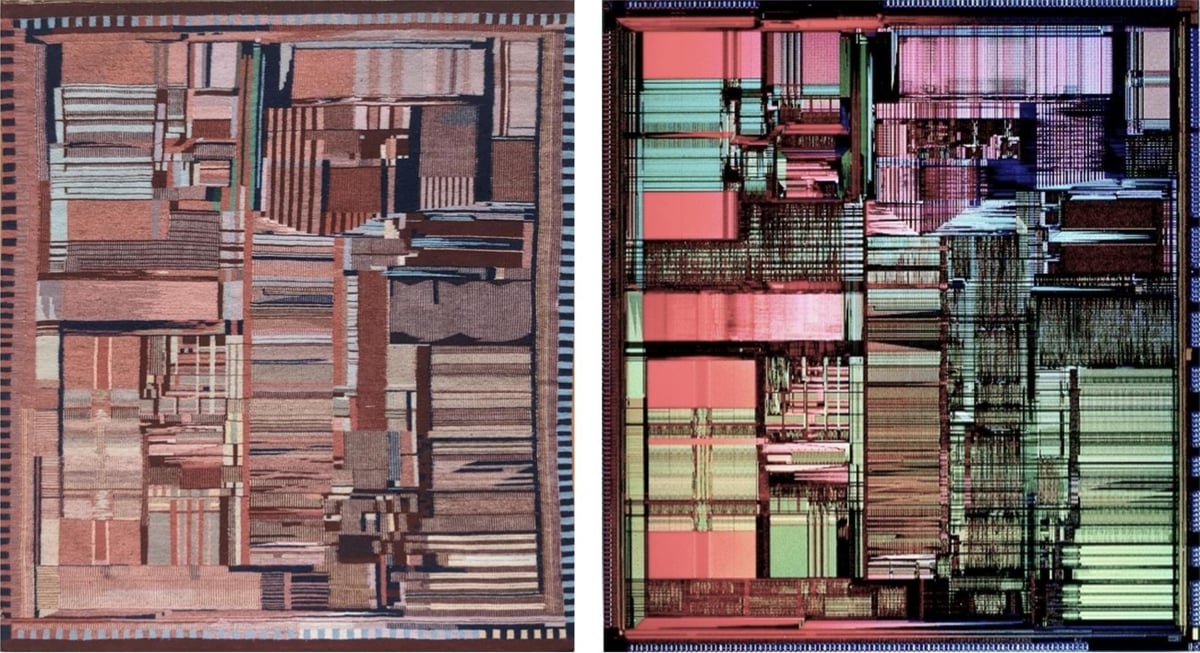
In 1994, a Navajo/Diné weaver named Marilou Schultz made a weaving of the microscopic pattern of an Intel Pentium processor. (In the image above, the weaving is on the left and the chip is on the right.)
The Pentium die photo below shows the patterns and structures on the surface of the fingernail-sized silicon die, over three million tiny transistors. The weaving is a remarkably accurate representation of the die, reproducing the processor’s complex designs. However, I noticed that the weaving was a mirror image of the physical Pentium die; I had to flip the rug image below to make them match. I asked Ms. Schultz if this was an artistic decision and she explained that she wove the rug to match the photograph. There is no specific front or back to a Navajo weaving because the design is similar on both sides,3 so the gallery picked an arbitrary side to display. Unfortunately, they picked the wrong side, resulting in a backward die image.
Schultz is working on a weaving of another chip, the Fairchild 9040, which was “built by Navajo workers at a plant on Navajo land”.
In December 1972, National Geographic highlighted the Shiprock plant as “weaving for the Space Age”, stating that the Fairchild plant was the tribe’s most successful economic project with Shiprock booming due to the 4.5-million-dollar annual payroll. The article states: “Though the plant runs happily today, it was at first a battleground of warring cultures.” A new manager, Paul Driscoll, realized that strict “white man’s rules” were counterproductive. For instance, many employees couldn’t phone in if they would be absent, as they didn’t have telephones. Another issue was the language barrier since many workers spoke only Navajo, not English. So when technical words didn’t exist in Navajo, substitutes were found: “aluminum” became “shiny metal”. Driscoll also realized that Fairchild needed to adapt to traditional nine-day religious ceremonies. Soon the monthly turnover rate dropped from 12% to under 1%, better than Fairchild’s other plants.
The whole piece is really interesting and demonstrates the deep rabbit hole awaiting the curious art viewer. (via waxy)



Socials & More