“If It Doesn’t Shine In Your Face, You Don’t See Anything”
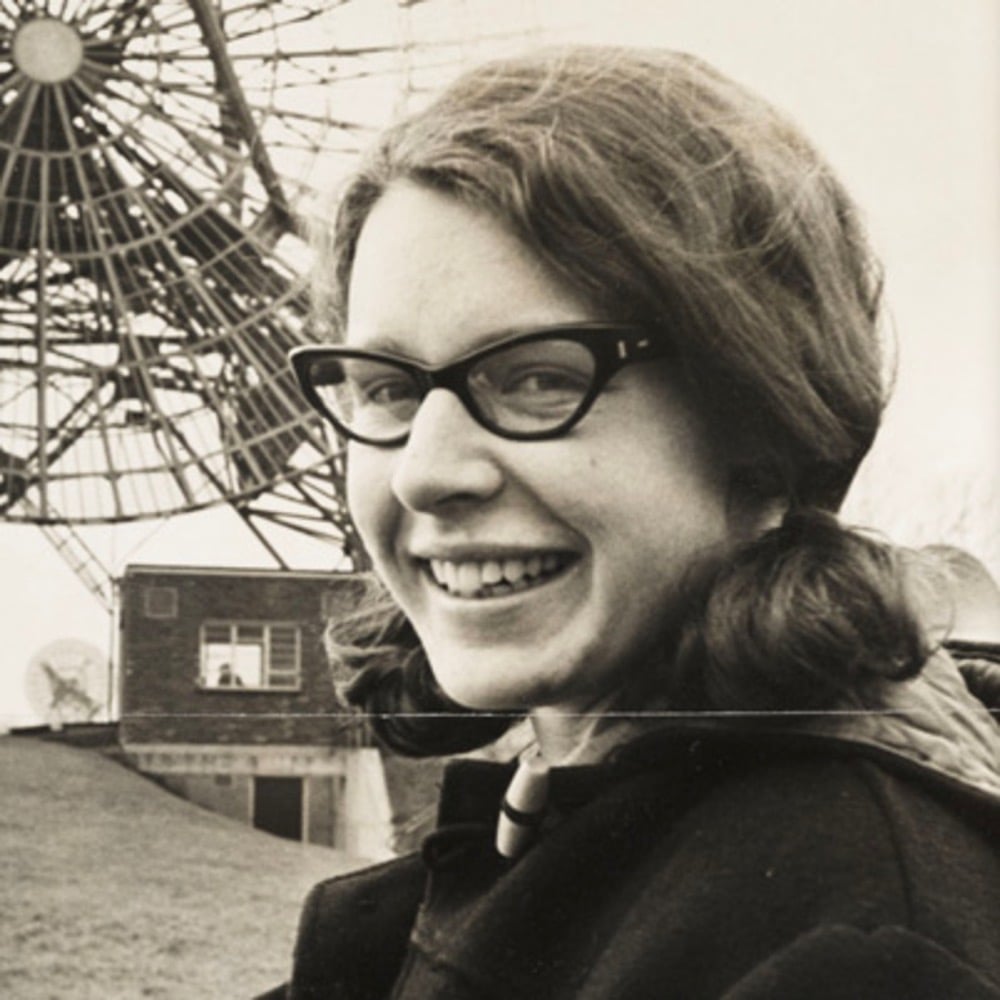

As I’ve written before, in the history of astronomy and astrophysics, women have made major discoveries and played a significant role in advancing our understanding of the universe but have often not gotten the recognition their male peers enjoy. In 1967, while she was working on her doctoral research with her advisor Antony Hewish, Jocelyn Bell Burnell (then Jocelyn Bell) discovered a new and unusual kind of object, the pulsar. In this short documentary, Bell Burnell shares her story — how she got interested in radio astronomy, the prejudice with which she was treated as the only woman in her university program, how she discovered the first pulsar and persisted (more than once) through Hewish’s assertions that the object was “interference”, and how she was passed over for the Nobel Prize for her discovery.
In 2018, Bell Burnell was awarded the Special Breakthrough Prize in Fundamental Physics “for fundamental contributions to the discovery of pulsars, and a lifetime of inspiring leadership in the scientific community”, joining past honorees like the LIGO team, Stephen Hawking, and the team that discovered the Higgs boson. She donated the entire $3 million prize to the Institute of Physics to help support “PhD physics students from under-represented groups” with their educations.
It’s not justice, but I will note that Bell Burnell’s Wikipedia page is longer and more substantial than Hewish’s, despite his Nobel.




Socials & More