Medieval History with Africa at the Center, Europe at the Margins
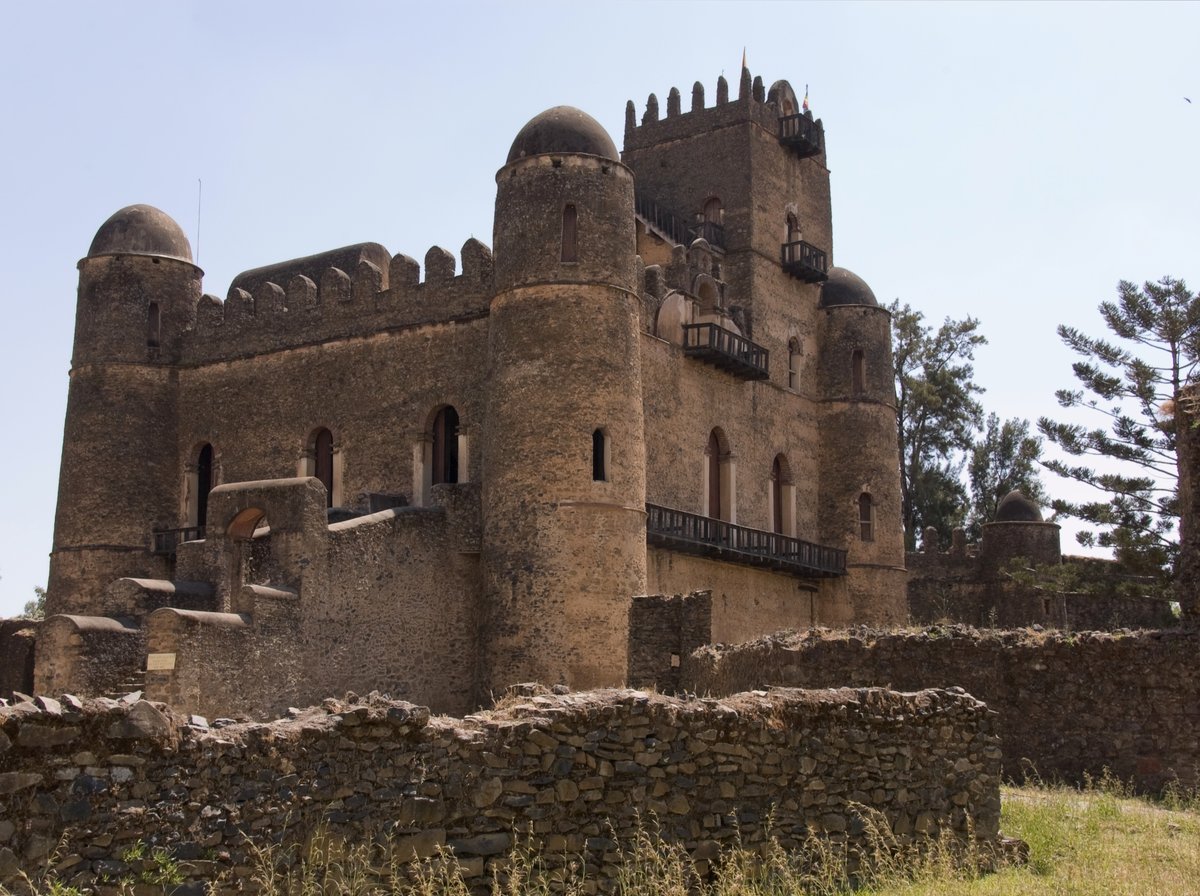

A new history of late medieval Ethiopia and its interactions with Europe by historian Verena Krebs does something a little unusual, at least for a professor at a European university: it treats the horn of Africa as the center of civilization that it was, and Europeans as the members of far-flung satellite states that Ethiopians could not help but see them as being.
It’s not that modern historians of the medieval Mediterranean, Europe and Africa have been ignorant about contacts between Ethiopia and Europe; the issue was that they had the power dynamic reversed. The traditional narrative stressed Ethiopia as weak and in trouble in the face of aggression from external forces, especially the Mamluks in Egypt, so Ethiopia sought military assistance from their fellow Christians to the north—the expanding kingdoms of Aragon (in modern Spain), and France. But the real story, buried in plain sight in medieval diplomatic texts, simply had not yet been put together by modern scholars. Krebs’ research not only transforms our understanding of the specific relationship between Ethiopia and other kingdoms, but joins a welcome chorus of medieval African scholarship pushing scholars of medieval Europe to broaden their scope and imagine a much more richly connected medieval world.
The Solomonic kings of Ethiopia, in Krebs’ retelling, forged trans-regional connections. They “discovered” the kingdoms of late medieval Europe, not the other way around. It was the Africans who, in the early-15th century, sent ambassadors out into strange and distant lands. They sought curiosities and sacred relics from foreign leaders that could serve as symbols of prestige and greatness. Their emissaries descended onto a territory that they saw as more or less a uniform “other,” even if locals knew it to be a diverse land of many peoples. At the beginning of the so-called Age of Exploration, a narrative that paints European rulers as heroes for sending out their ships to foreign lands, Krebs has found evidence that the kings of Ethiopia were sponsoring their own missions of diplomacy, faith and commerce.
In fact, it would probably be accurate to say that Ethiopia (which over its long history has included areas now in Eritrea, Somalia, Sudan, Yemen, and parts of Saudi Arabia) was undergoing its own Renaissance, complete with the rediscovery of a lost classical kingdom, Aksum (sometimes called Axum).
Around the third century, Aksum was considered an imperial power on the scale of Rome, China, and Persia. It was part to better understand the historical legacy of Aksum that east Africans circa 1400 reestablished trading ties and military partnerships with their old Roman trading partners — or, in their absence, the Germanic barbarians who’d replaced them.
Europe, Krebs says, was for the Ethiopians a mysterious and perhaps even slightly barbaric land with an interesting history and, importantly, sacred stuff that Ethiopian kings could obtain. They knew about the Pope, she says, “But other than that, it’s Frankland. [Medieval Ethiopians] had much more precise terms for Greek Christianity, Syriac Christianity, Armenian Christianity, the Copts, of course. All of the Orthodox and Oriental Orthodox churches. But everything Latin Christian [to the Ethiopians] is Frankland.”




Stay Connected