Previously Unpublished Photos of Indigenous Culture in Alaska Circa 1927
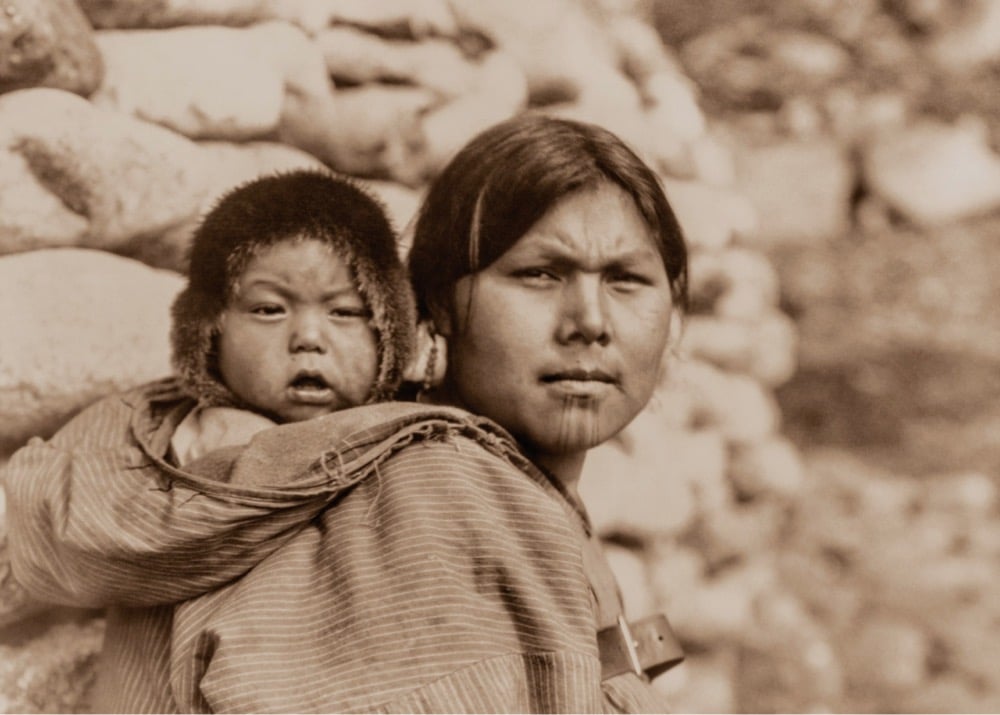
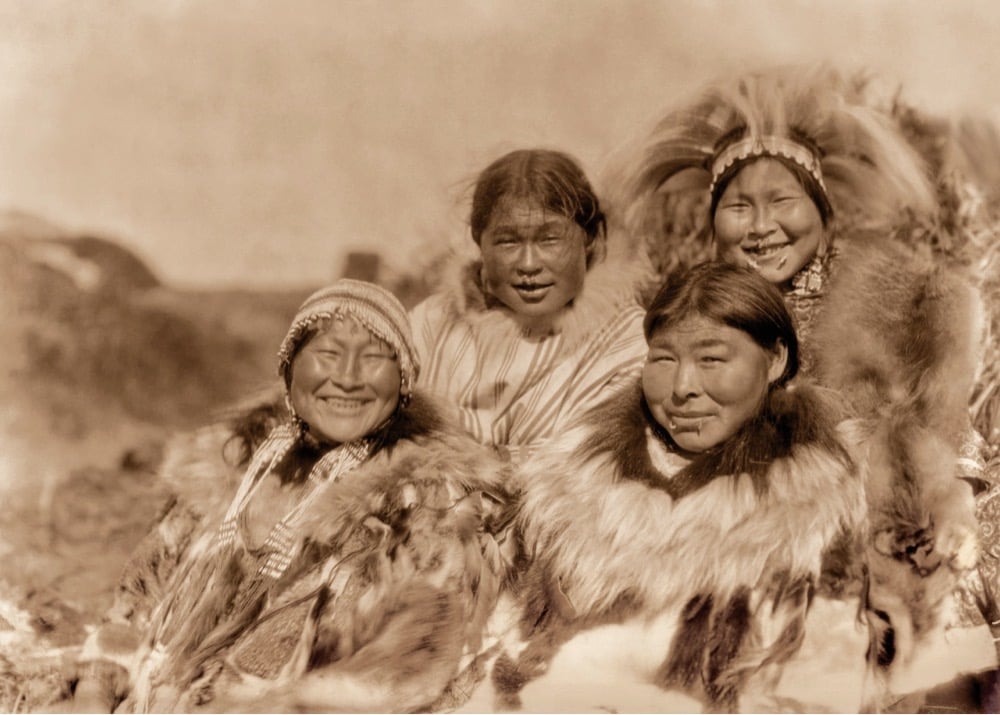
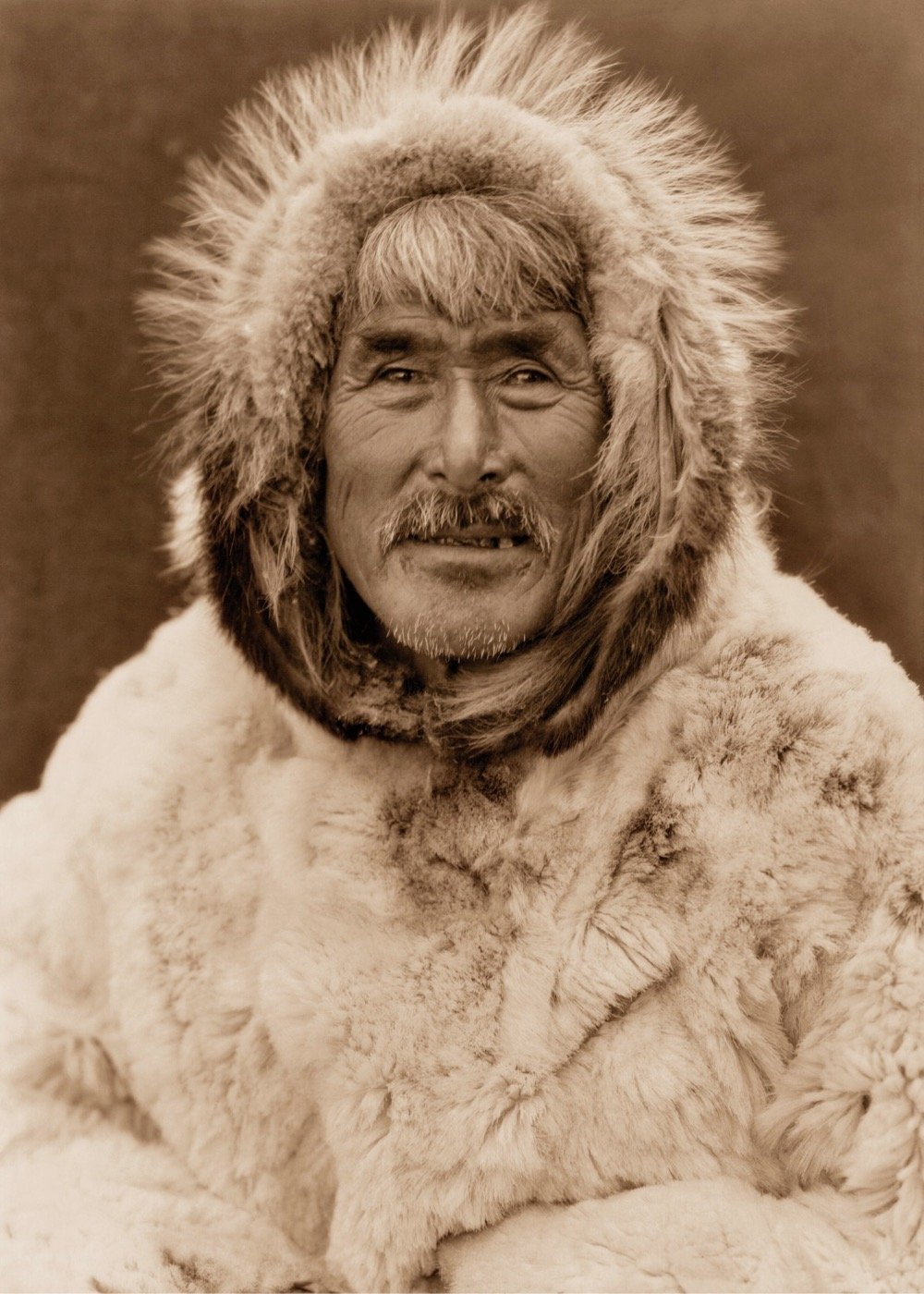



In 1927, photographer and ethnologist Edward S. Curtis travelled to the US territory of Alaska to photograph indigenous peoples and their cultures for his seminal work, The North American Indian. Some of the photos he took in Alaska were never published and make up a new exhibition at the Muskegon Museum of Art, Edward S. Curtis: Unpublished Alaska, The Lost Photographs.
Begun in 1906, The North American Indian was the defining passion of Curtis’s life, an attempt to record, in writing and photography, the lives of the Indigenous peoples of the Southwestern, Western, and Northwestern United States. This trip, planned for a single season, would be the final voyage to complete his epic quest. Curtis took hundreds of images on his journey, only part of which were ultimately published. The rest sat, unseen, passed down through the family until today.
Edward Curtis: Unpublished Alaska, The Lost Photographs presents, for the first time to the public, images made from the unused original negatives. Over 100 images will comprise the exhibition, along with excerpts from the personal journals of Curtis and his daughter Beth that describe their often harrowing adventures in the Bering Sea.
You can see a selection of these photos online here and previously published photos by Curtis in Northwestern’s archive.
Update: Curtis’s photos are the subject of controversy and criticism, some of which you can read about here.
The North American Indian is a seminal and controversial blend of documentary and staged photography — one which contributes to much of the foundational imagery and, often-stereotypical, understanding possessed by white America about some 82-plus native tribes that the United States eradicated over a century of colonization. Much has been made about the complexities, contradictions, and conflicts of interest in Curtis’s masterwork, by Native and non-Native scholars. Some argue that in staging photographs and, at times, adding props or accessories, Curtis took liberties with the concept of ethnography, both imposing and reinforcing white notions of Native American appearances and culture. Others argue that without Curtis, there would be hardly any extant imagery of the cultural heritage of the tribes he worked with.




Socials & More