The Rapidly Falling Cost of Solar Energy Visualized
Check out this graph from Our World in Data of the price of electricity from new power plants. In 2009, solar was the most expensive energy source and in 2019 it’s the cheapest.
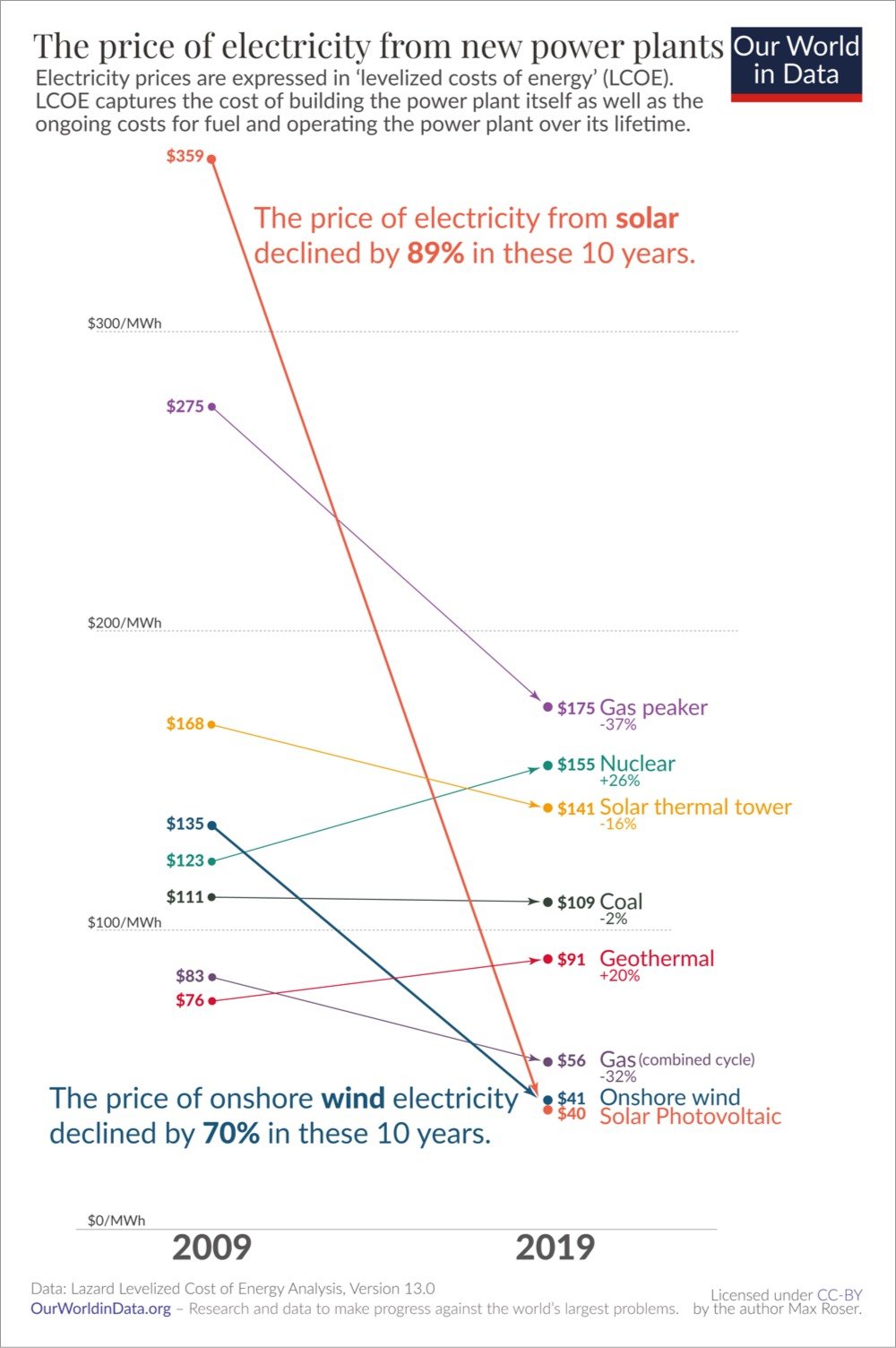
Electricity from utility-scale solar photovoltaics cost $359 per MWh in 2009. Within just one decade the price declined by 89% and the relative price flipped: the electricity price that you need to charge to break even with the new average coal plant is now much higher than what you can offer your customers when you build a wind or solar plant.
It’s hard to overstate what a rare achievement these rapid price changes represent. Imagine if some other good had fallen in price as rapidly as renewable electricity: Imagine you’d found a great place to live back in 2009 and at the time you thought it’d be worth paying $3590 in rent for it. If housing had then seen the price decline that we’ve seen for solar it would have meant that by 2019 you’d pay just $400 for the same place.
The rest of the page is worth a read as well. One reason why the cost of solar is falling so quickly is that the technology is following a similar exponential curve to computer chips, which provide more speed and power every year for less money, an observation called Wright’s Law:
If you want to know what the future looks like one of the most useful questions to ask is which technologies follow Wright’s Law and which do not.
Most technologies obviously do not follow Wright’s Law — the prices of bicycles, fridges, or coal power plants do not decline exponentially as we produce more of them. But those which do follow Wright’s Law — like computers, solar PV, and batteries — are the ones to look out for. They might initially only be found in very niche applications, but a few decades later they are everywhere.
If you are unaware that technology follows Wright’s Law you can get your predictions very wrong. At the dawn of the computer age in 1943 IBM president Thomas Watson famously said “I think there is a world market for maybe five computers.” At the price point of computers at the time that was perhaps perfectly true, but what he didn’t foresee was how rapidly the price of computers would fall. From its initial niche when there was perhaps truly only demand for five computers they expanded to more and more applications and the virtuous cycle meant that the price of computers declined further and further. The exponential progress of computers expanded their use from a tiny niche to the defining technology of our time.
Solar modules are on the same trajectory, as we’ve seen before. At the price of solar modules in the 1950s it would have sounded quite reasonable to say, “I think there is a world market for maybe five solar modules.” But as a prediction for the future this statement too would have been ridiculously wrong.




Stay Connected