Horizontal history
At Wait But Why, Tim Urban turns history on its side by thinking about time-synchronized events around the world, as opposed to events through the progression of time in each part of the world.
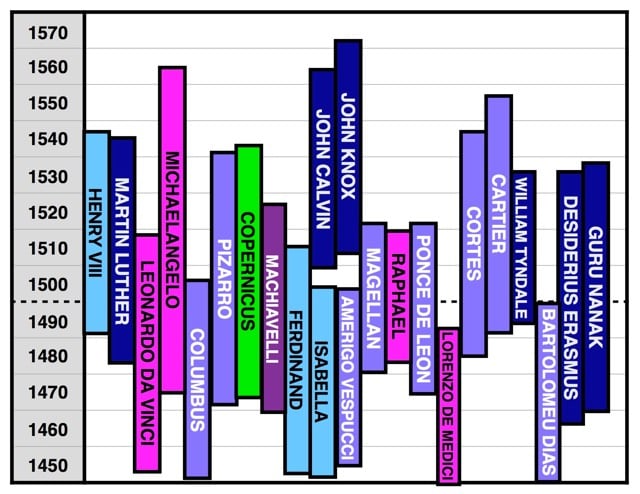
Likewise, I might know that Copernicus began writing his seminal work On the Revolutions of the Celestial Spheres in Poland in the early 1510s, but by learning that right around that same time in Italy, Michelangelo painted the ceiling of the Sistine Chapel, I get a better picture of the times. By learning that it was right while both of these things were happening that Henry VIII married Catherine of Aragon in England, the 1510s suddenly begins to take on a distinct personality. These three facts, when put together, allow me to see a more three-dimensional picture of the 1510s — it allows me to see the 1510s horizontally, like cutting out a complete segment of the vine tangle and examining it all together.
He does this mainly by charting and graphing the lifetimes of famous people, revealing hidden contemporaries.
I’ve been slowly making my way through Ken Burns’ remastered The Civil War.1 At a few points in the program, narrator David McCullough reminds the viewer of what was going on around the world at the same time as the war. In the US, 1863 brought the Battle of Gettysburg and The Emancipation Proclamation. But also:
In Paris that year, new paintings by Cezanne, Whistler, and Manet were shown at a special exhibit for outcasts. In Russia, Dostoevsky finished Notes from the Underground. And in London, Karl Marx labored to complete his masterpiece, Das Kapital.
And a year later, while the advantage in the war was turning towards the US:1
In 1864, a rebellion in China that cost 20 million lives finally came to an end. In 1864, the Tsar’s armies conquered Turkistan and Tolstoy finished War and Peace. In 1864, Louis Pasteur pasteurized wine, the Geneva Convention established the neutrality of battlefield hospitals, and Karl Marx founded the International Workingmen’s Association in London and in New York.
Urban explicitly references the war in his post:
People in the US associate the 1860s with Lincoln and the Civil War. But what we overlook is that the 1860s was one of history’s greatest literary decades. In the ten years between 1859 and 1869, Darwin published his world-changing On the Origin of Species (1859), Dickens published A Tale of Two Cities (1859) and Great Expectations (1861), Lewis Carroll published Alice in Wonderland (1865), Dostoyevsky published Crime and Punishment (1866), and Tolstoy capped things off with War and Peace (1869).
The Civil War. The Origin of Species. Alice in Wonderland. The infancy of Impressionism. Pasteurization. Das Kapital. Gregor Mendel’s laws of inheritance. All in an eight-year span. Dang.
Which is simply excellent. I had forgotten how powerful the storytelling technique Burns devised for his documentaries is. Really really worth your time to watch or re-watch.↩
In talking about the Civil War, I’ve been trying to use Michael Todd Landis’ new language…so, “labor camps” instead of “plantations” and “United States” instead of “Union”.↩




Stay Connected